Figure 5.
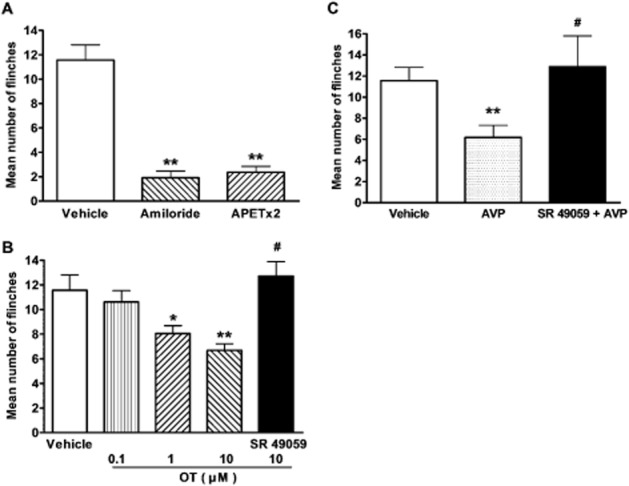
Effects of OT and AVP on nociceptive responses to intraplantar injection of acetic acid in rats. Intraplantar injection of acetic acid (0.6%, 20 μL) evoked a flinch/shaking response in female rats. The bar graph in (A) shows acidosis-evoked pain was blocked by pretreatment with 200 μM amiloride and 20 μM APETx2. **P < 0.01, unpaired t-test, compared with vehicle column. n = 10 in each column. The bar graph in (B) shows that pretreatment with OT decreased flinching behaviour induced by acetic acid in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of OT was blocked by SR49059, a selective V1A receptor antagonist. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way anova followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test, compared with vehicle column; #P < 0.01, post hoc Bonferroni's test, compared with OT (10 μM) column. n = 10 in each column. The bar graph in (C) shows that pretreatment with 10 μM AVP also decreased flinching behaviour induced by acetic acid, and SR49059 completely blocked the analgesia of AVP on acetic acid-induced pain. **P < 0.01, one-way anova followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test, compared with vehicle column; #P < 0.01, post hoc Bonferroni's test, compared with AVP column. n = 10 in each column. Flinch/shaking of paw was recorded as the number of flinches per observation period (5 min).
