FIGURE 2:
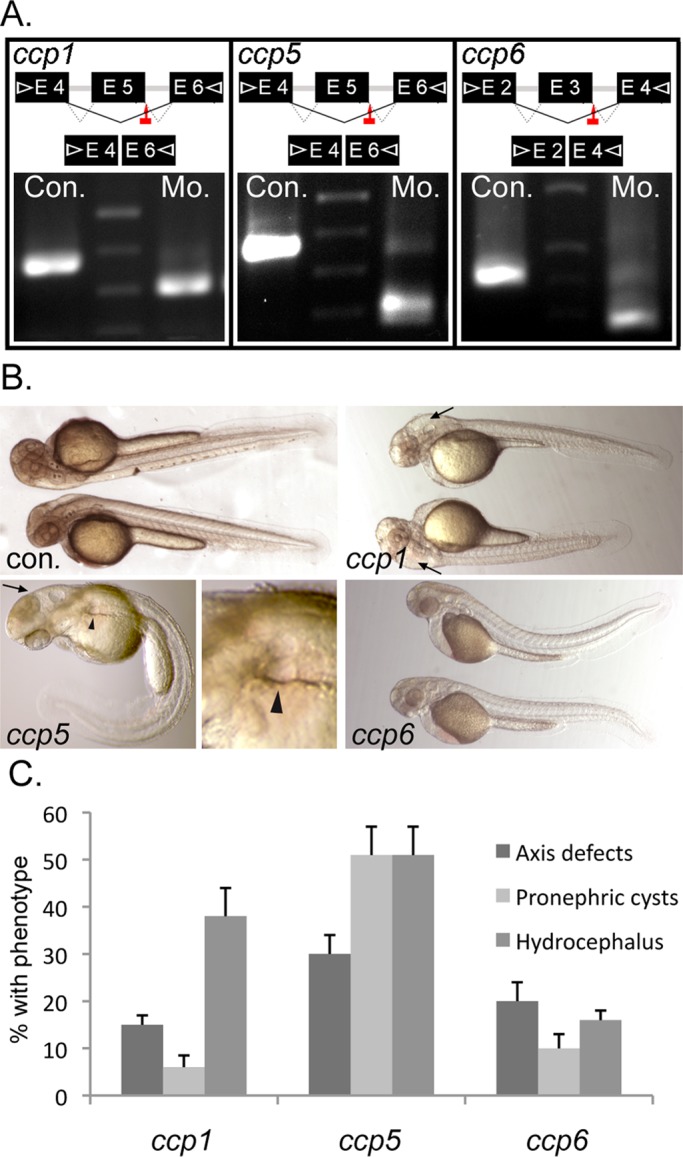
ccp5 knockdown alone induces the typical spectrum of ciliopathy phenotypes in wild-type zebrafish. (A) Splice donor sites targeted by antisense morpholinos (red arrows) in ccp1, ccp5, and ccp6 genes and agarose gel analysis showing RT-PCR amplicons of ccp1, ccp5, and ccp6 generated using primer pairs (arrowheads) in indicated exons were smaller in morphant (Mo.) embryos than in respective control (Con.) In each case, the reduced size of morphant amplicon relative to control matched the size of the deleted target exon. (B) External morphology of 2.5-d-old zebrafish injected with optimal dose of control or antisense morpholinos designed to knock down ccp1, ccp5, and ccp6 genes, respectively. (C) Frequency of phenotype associated with cilia defects. ccp1 morphants mostly exhibit isolated hydrocephalus, whereas ccp5 morphants exhibit hydrocephalus and pronephric cysts, often with acutely curved body axis. Replicates: ccp1×5Mo (n = 181 embryos/4 injections); ccp5×5Mo (n = 275 embryos/5 injections); ccp6×3Mo (n = 261embryos/5 injections).
