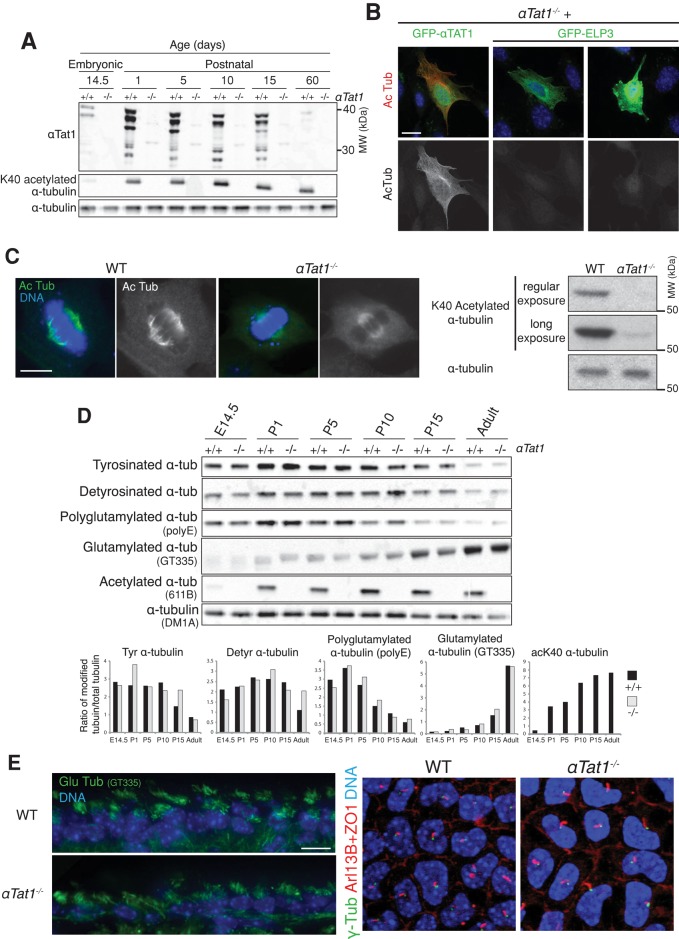
FIGURE 1:
αTat1 is the major α-tubulin K40 acetyltransferase in vivo and is dispensable for mammalian CNS development and ciliogenesis. (A) Brain lysates from various developmental stages (E14.5, embryonic day 14.5; P1–P15, postnatal days 1–15) were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (B) αTat1−/− MEFs were transfected with GFP-αTat1 or GFP-ELP3 (green) and immunostained for GFP (green) and K40 acetylated α-tubulin (red). (C) Left, K40 acetylated α-tubulin immunostaining (green) of αTat1+/+ and αTat1−/− MEFs. Right, αTat1+/+ and αTat1−/− MEFs lysates were immunoblotted for K40 acetylated and total α-tubulin. (D) Brain lysates from αTat1+/+ and αTat1−/− mice at various developmental stages were immunoblotted for various α-tubulin posttranslational modifications. The quantitation of the immunoblots showed no major differences between wild-type and knockout mice. (E) Left, adult brain cryosections were stained with polyglutamylated α-tubulin (GT335 antibody, ependymal motile cilia, green). Right, basal bodies (γ-tubulin, green), primary cilia (Arl13B, red) and the cell–cell junction (ZO-1, red) were labeled in P6 corneal endothelium whole mounts. No defects in motile or primary cilia presence were noted in αTat1−/− mice. Scale bars: B, 20 μm; C, 10 μm; E, 10 μm.