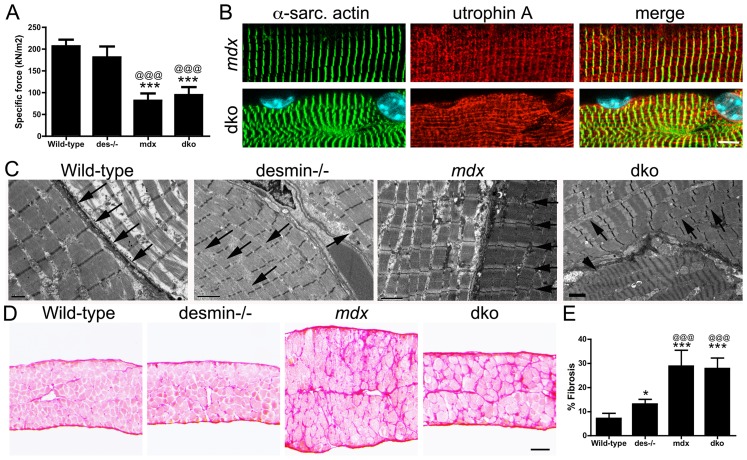
Figure 9. Impaired diaphragm function in the dko correlates with loss of sarcomere alignment and deposition of collagen.
A) Mean +/− S.D. specific force of diaphragm strips in vitro from wild-type (n = 6), desmin−/− (n = 5), mdx4cv (n = 5) and dko (n = 5) mice. B) Utrophin A colocalizes with α-sarcomeric actin in longitudinal sections. Note the misalignment of α-sarcomeric actin and utrophin A in the dko myofiber. Scale bar = 6 µm. C) Electron microscopy of longitudinal sections of diaphragm muscle demonstrating the alignment of sarcomeres in wild-type and mdx mice (arrows). Note the alignment of sarcomeres is perturbed in desmin−/− muscles (arrows) and severely impaired in the dko muscles (arrows point to misalignment of sarcomeres while the arrow head points toward a hyper-contracted myofiber). Scale bars = 2 µm. D) Sirius red staining of collagen in transverse frozen sections of the wild-type (n = 8), desmin−/− (n = 9), mdx4cv (n = 5) and dko (n = 5) diaphragms. Scale bar = 100 µm. E) Mean +/− S.D. of Sirius red staining as a proportion of the muscle area. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 compared to wild-type, @@@P<0.001 compared to desmin−/−.