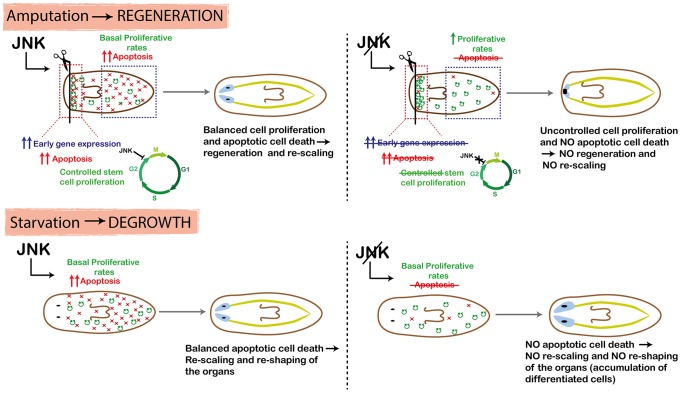
Figure 8. Schematic showing role of JNK in planarian regeneration and homeostatic degrowth.
In the wound region, JNK triggers early-gene expression and apoptosis, and mediates temporal control of the cell cycle progression of neoblasts, which ensures the balanced differentiation of different cell types and hence proper regeneration of missing tissues. In pre-existing regions, JNK triggers apoptosis and maintains basal levels of proliferation to ensure that body proportion is properly restored after amputation. RNA interference of JNK activity prevents all these processes in both the wound region and in pre-existing regions, as well as regeneration and rescaling.