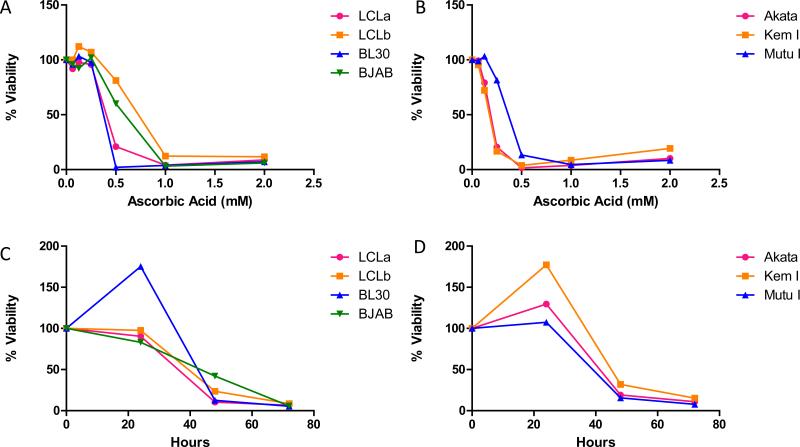
Figure 1. Ascorbic acid kills EBV-positive and EBV-negative cell lines.
A and B. Cells were treated with various concentrations of ascorbic acid for 72 hr and cell viability was analyzed using alamar blue. Ascorbic acid killed EBV transformed (LCLa and LCLb), EBV-negative Burkitt lymphoma (BL30 and BJAB), and EBV-positive Burkitt lymphoma (Akata, Kem I, and Mutu I) cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. A representative experiment is shown in which each point represents the mean of triplicate replicates. C and D. Cells were treated with treated with 2 mM ascorbic acid for 24, 48, or 72 hr and cell viability was analyzed using alamar blue. For all cell lines tested, ascorbic acid induced cell death increased with length of treatment. A representative experiment is shown in which each point represents the mean of triplicate replicates.