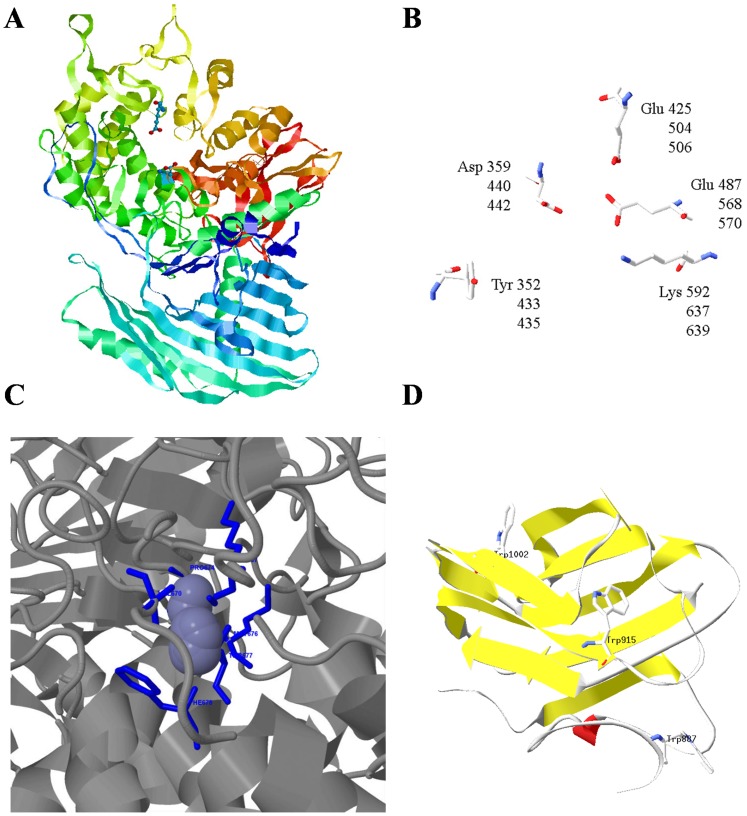
Figure 3. Structural analysis of CpAtc1 protein.
(A) Ribbon representation. Colour-ramped from the N terminus (blue) to the C terminus (red). The residues proposed to act in the hydrolysis mechanism (Asp440 and Glu568) are shown in ball-and-stick representation. The output structure was generated with RasMol (Sayle and Milner-White, 1995). (B) Superimposition of the important active site molecules of Lactobacillus brevis maltose phosphorylase pdb:1H54, C. parapsilosis and C. albicans (Labels are shown in order). The figure represents the best fit between the three molecules. The structure was generated with the Swiss Pdb-viewer (Guex and Peitsch, 1997). (C) 3DLigandSite visualization of prediction for the CpAtc1 structure with predicted binding site for Zn (blue). The ligands in the cluster used to make the prediction are displayed with ions in spacefill and organic molecules in wireframe formats. (D) Putative homology model for the CpAtc1CBM from C. parapsilosis covering residues 854 to 1039. The residues proposed to participate in the binding site (Trp887, Trp915 and Trp1002) are shown in ball-and-stick representation. The structure was generated with the Swiss Pdb-viewer (Guex and Peitsch, 1997).