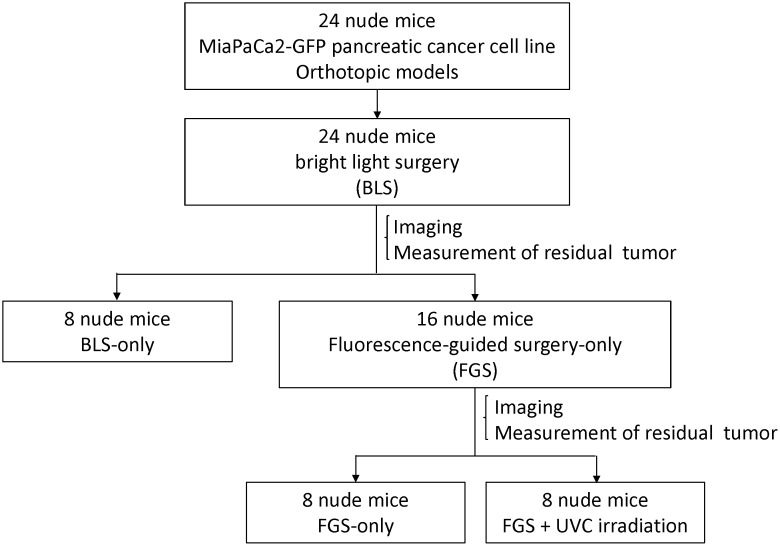
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental protocol.
Two weeks after orthotopic implantation of MiaPaCa-2-GFP pancreatic cancer, bright-light surgery (BLS) was performed on all tumor-bearing mice (n = 24). Postoperatively, the surgical resection bed was imaged with the OV100 at a magnification of 0.56x to detect residual tumor. Mice which underwent BLS were randomized into 3 treatment groups: BLS-only (n = 8), FGS (n = 8), or FGS-UVC (n = 8). Residual tumors in mice in the FGS and FGS-UVC groups were resected using the Dino-Lite imaging system under fluorescence navigation. After completion of FGS, the surgical resection bed was imaged with the OV100 at a magnification of 0.89x to detect micoscopic minimal residual cancer (MRC). The surgical resection bed in the mice in the FGS-UVC group was irradiated with 2700 J/m2 UVC (emission peak, 254 nm) from the bottom of the chamber using a Benchtop 3UV transilluminator (UVP, LLC, Upland, CA).