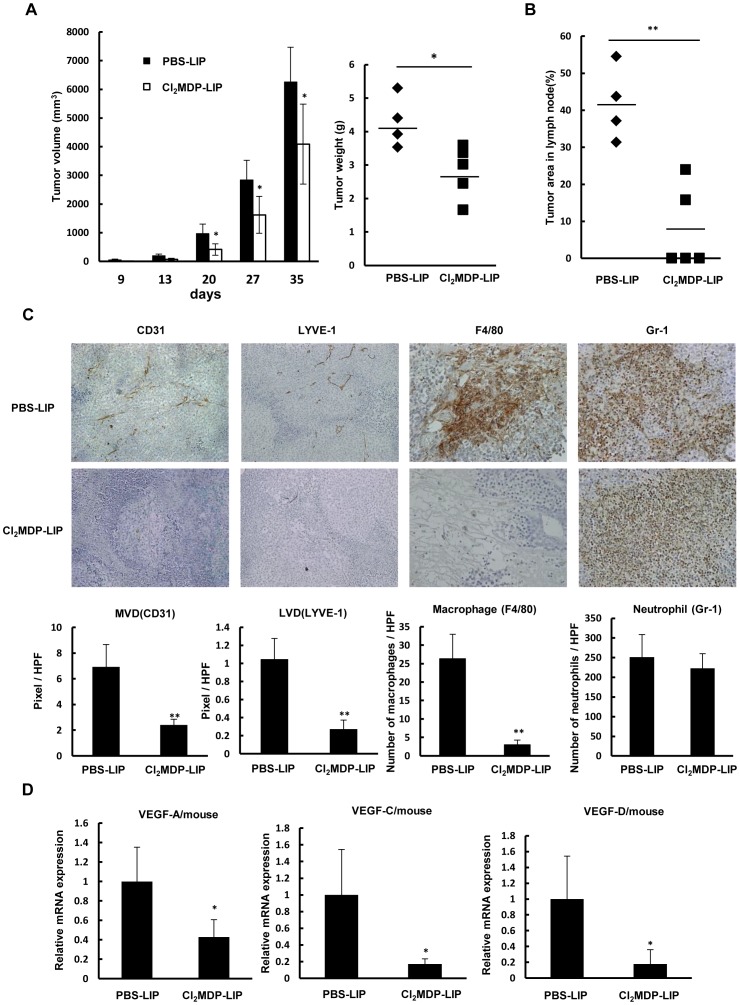
Figure 3. Effect of macrophage depletion on tumor growth, lymph node metastasis, and VEGF-A and VEGF-C expression.
(A) Anti-tumor effect of Cl2MDP-LIP on tumor growth by LNM35 xenografts. Mice were subcutaneously inoculated with LNM35 cells at day 0, and tumor growth was followed until day 35 in animals intravenously injected twice weekly with PBS-LIP or Cl2MDP-LIP. *p<0.05 between PBS-LIP and Cl2MDP-LIP-treated groups (n = 5 mice per group). (B) Inhibitory effect of Cl2MDP-LIP on lymph node metastasis. The area occupied by cancer cells in the lymph node was determined by H&E staining. Relative tumor area is expressed as the percent of the total lymph node area (n = 5 mice per group); **p<0.01 compared with the PBS-LIP-treated group. (C) Effect of Cl2MDP-LIP on angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and macrophage and neutrophil infiltration by LNM35 tumors. IHC analysis was performed on day 35 using specific antibodies for vascular endothelium (CD31), lymphatic vessels (LYVE-1), infiltrated macrophages (F4/80), and infiltrated neutrophils (Gr-1). Five areas of each tumor section from five tumor samples were quantitatively analyzed; **p<0.01. (D) Effect of Cl2MDP-LIP on the expression of mouse VEGF-A, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D mRNA in LNM35 tumors, determined by qRT-PCR analysis of five tumors on day 35; *p<0.05 compared with the PBS-LIP-treated group.