Figure 7.
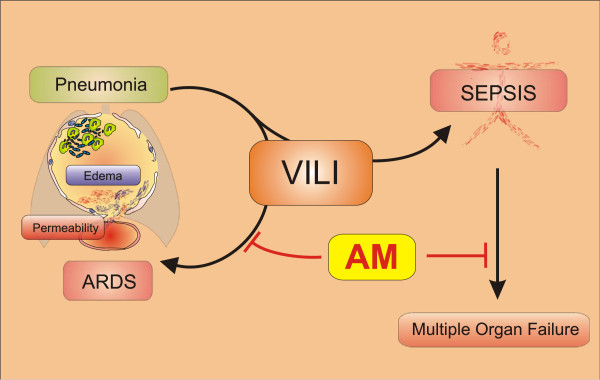
Mechanical ventilation drives pneumococcal pneumonia into lung injury and sepsis: protection by adrenomedullin. Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) led to substantial aggravation of previously established severe pneumonia resulting in acute respiratory failure, which was accompanied by elevation of pulmonary cytokine levels independent from leukocyte recruitment or bacterial replication in the lung. Adrenomedullin (AM) protected against development of lung injury without having anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial functions, probably by mediating vascular barrier protection and stabilization of microcirculation. VILI induced the development of sepsis and related multiple organ failure, which was avoided by AM. ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome.
