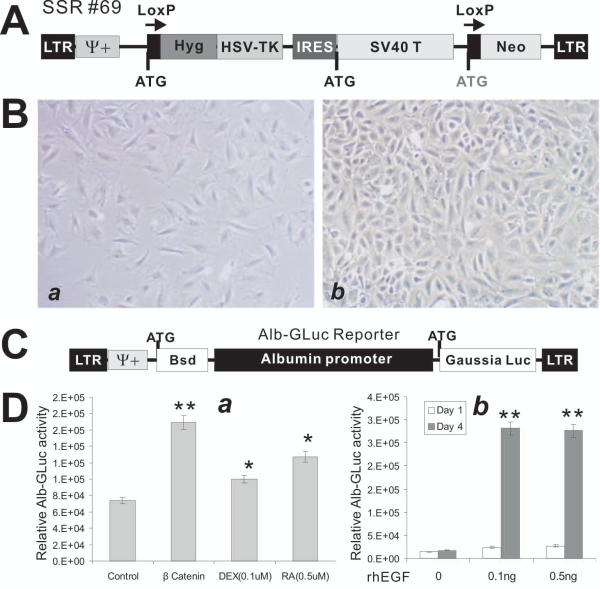
Figure 2.
Establishment and characterization of immortalized mouse fetal hepatic progenitor cells (iHPCs). (A) Schematic representation of the reversible immortalization retroviral vector SSR#69 26-28. (B) Growth and morphological features of the primary (a) and the immortalized HPCs (iHPCs) (b). The immortalization was carried out as described 23,24. The cells were seeded at the same density and were photographed at day 4 after plating. Representative images are shown. (C) Construction of an albumin promoter-driven Gaussia luciferease reporter (Alb-GLuc). A 2.5kb fragment containing the mouse albumin promoter region was cloned in front of Gaussia luciferase, resulting in the Alb-GLuc reporter, which was used to make stable Alb-GLuc reporter lines. (D) The Alb-GLuc reporter is used to monitor the differentiation status of the iHPCs. Several known hepatic differentiation factors, including β-catenin, dexamethasone, and retinoic acid (a) and rhEGF (b), were shown to induce Alb-GLuc activities. “*”, p-value < 0.05; “**”, p-value < 0.001.