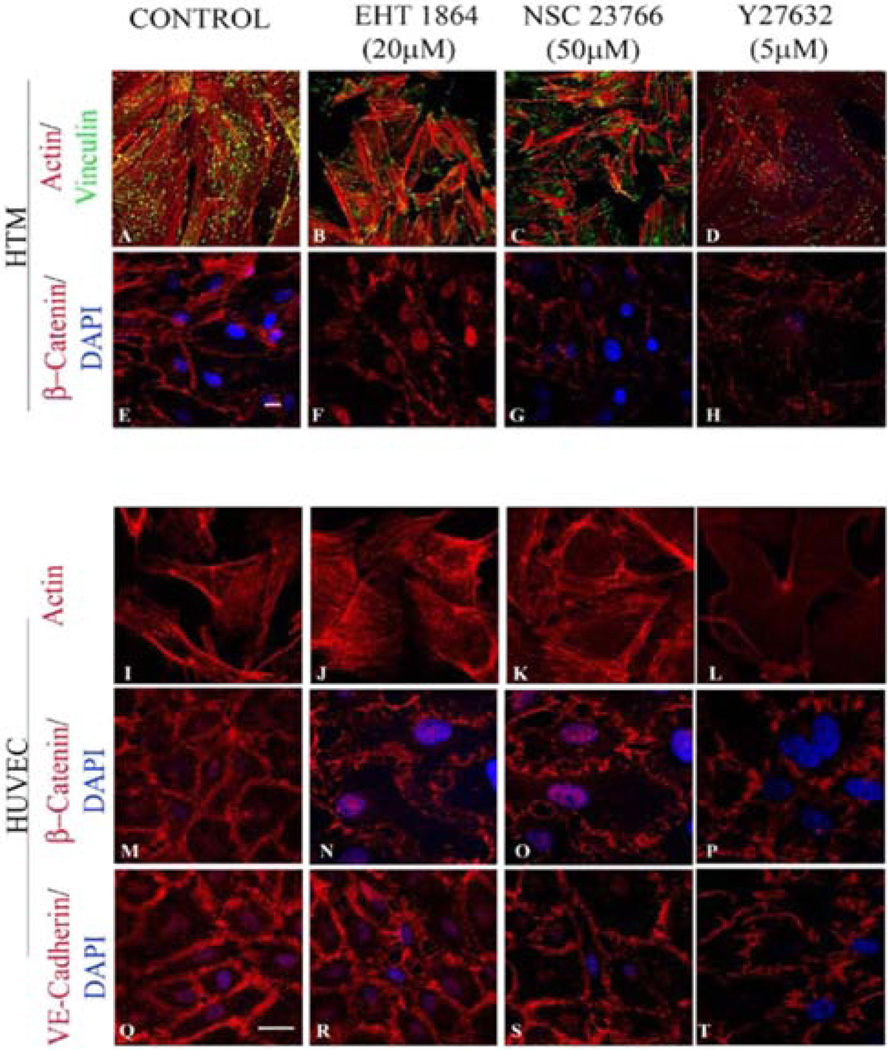
Figure 2.
Rac GTPase inhibitor-induced effects on actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesions, and adherens junctions in HTM and HUVEC cells. Confluent cultures of HTM and HUVEC cells maintained overnight in 1% FBS were treated with either Rac inhibitors EHT1864 at 20 µM (B, F, J, N, R) or NSC23766 at 50 µM (C, G, K, O, S), or with Rho kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) at 5 µM (D, H, L, P, T) for 4 h. EHT1864 and NSC23766 both induced reorganization of actin stress fibers (Rhodamine-phalloidin staining; red) to the cell cortical region and clustering of focal adhesions (vinculin staining; green) to the leading edges in both HTM and HUVEC cells (B, C, J, K) compared to controls (A, I). In these cell types, Rho kinase inhibition led to cellular relaxation manifested by decreased actin stress fibers and focal adhesions (D, L). β-Catenin immunostaining was decreased in both HTM and HUVEC cells after treatment with Rac inhibitors (F, G, N, O) or Rho kinase inhibitor (H, P) and relative to controls (E, M). HUVEC cells showed a loss of VE-cadherin staining and increased intercellular gaps upon inhibition of Rac GTPase (R, S) or Rho kinase (T) and compared to the control (Q). Scale bar: 10 µm.