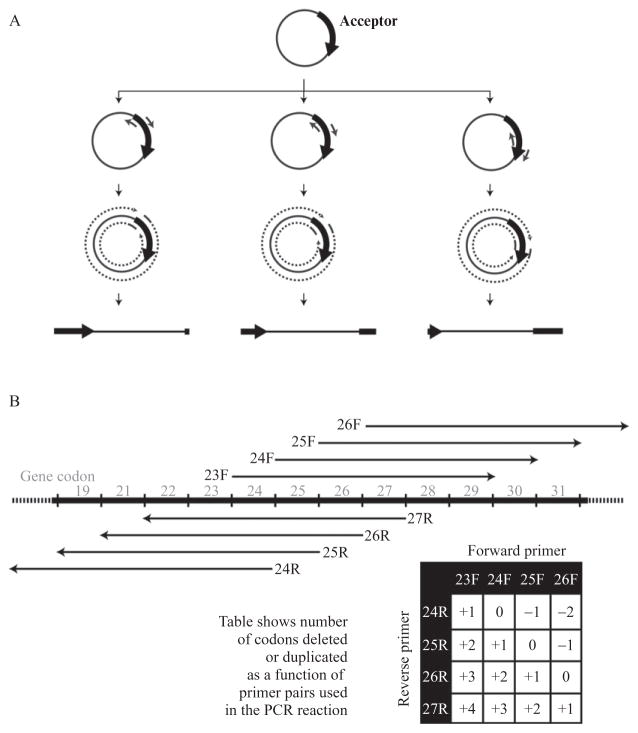
Figure 17.2.
Schematic depiction of multiplex inverse PCR. (A) Basic mechanism. PCR is performed with abutting sets of primers designed to amplify in opposite directions around the plasmid resulting in a set a linear plasmid dsDNA molecules whose site of linearization is defined by the primers. (B) Details of primer design and method for creation of deletions and duplications at the site of linearization. As an example, amplification using a set of four forward and four reverse primers is shown in the region around codons 19–31 of a gene. Different combinations of forward and reverse primers results in codon deletions or tandem duplications as indicated in the table.