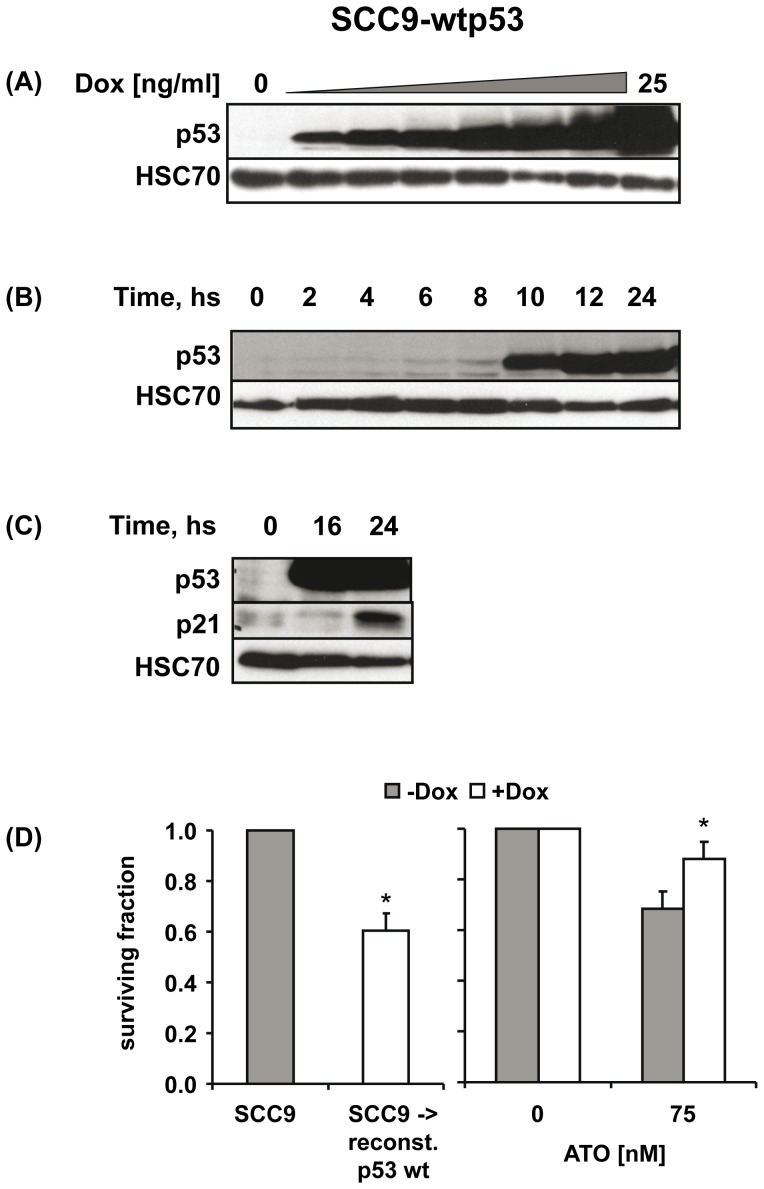
Figure 2. Reconstitution of p53-deficient SCC9 cells with wt p53 renders them less sensitive to ATO treatment.
(A) SCC9-wtp53 cells were treated with increasing doses of Dox for 24 hs or (B) with a dose of 20 ng/ml Dox for the indicated time periods. The expression of p53 was detected by immunoblotting. Detection of HSC70 served as protein loading control. (C) Induction of p53 by treatment of SCC9-wtp53 cells with 20 ng/ml Dox was followed by upregulation of p21. (D) Reconstitution of wt p53 after Dox treatment inhibited the clonogenic growth of SCC9 cells (left graph). After correction for this growth-inhibitory effect of wt p53 itself, a significantly reduced sensitivity of SCC9-wtp53 cells to ATO treatment (75 nM) was observed (right graph). * p<0.05 (paired t-test).