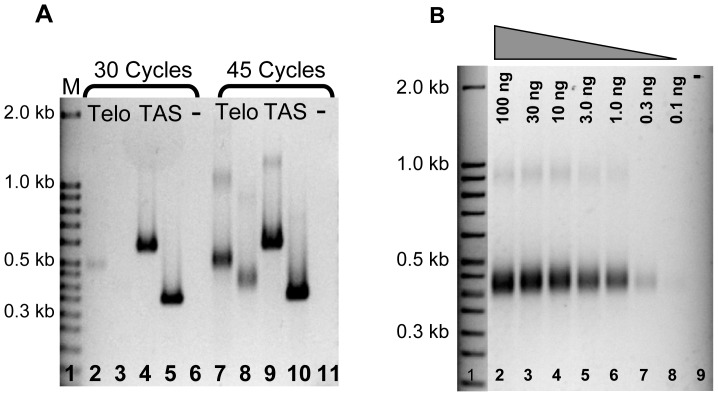
Figure 3. Determining the optimal conditions and sensitivity of the telomere-anchored PCR assay.
A. PCR products were amplified for 30 cycles (lanes 2–5) or 45 cycles (lanes 7–10). Though the two telomere-associated sequences were visible at both 30 and 45 cycles (lanes 4, 5, 9, 10), the telomeric sequences were clearly seen at 45 cycles (lanes 2, 3, 7, 8). PCR was performed using either forward primer A (lanes 2 and 7) or B (lanes 3 and 8) coupled with telomere-anchored PCR primer 4. Telomere-associated sequences were used as controls in lanes 4, 5, 9, and 10. B. Diluted genomic DNA, ranging from 100 ng to 0.1 ng (lanes 2–8), was tailed and subjected to PCR analysis, and the intensity of PCR products was observed at a DNA concentration as low as 0.1 ng. PCR was performed using forward primer B coupled with telomere-anchored PCR primer 4.