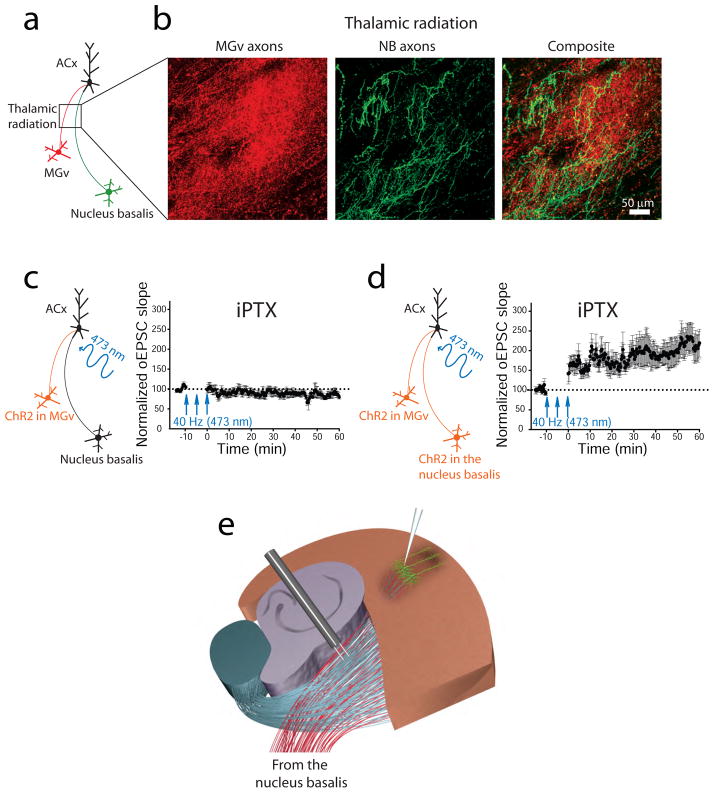
Figure 6. Thalamic radiation contains thalamic projections from the auditory thalamus and cholinergic projections from the nucleus basalis.
(a) Diagram shows the expression of a red fluorescent protein in the auditory thalamus (MGv) excitatory neurons and a green fluorescent protein in the nucleus basalis (NB) cholinergic neurons. (b) Thalamic and cholinergic projections are visualized in the thalamic radiation. (c, left) Diagram showing that channelrhodopsin 2 (ChR2) is expressed in the MGv excitatory neurons only. (c, right) A 40-Hz pattern of light-activated thalamic projections in the presence of cortical dysinhibition via picrotoxin (iPTX) is not sufficient to induce TC LTP of light-activated excitatory postsynaptic currents (oEPSCs) (d, left) Diagram showing that ChR2 is expressed in both the MGv excitatory neurons and NB cholinergic neurons (Chun and others, 2013). (d, right) Stimulation of thalamic projections paired with cholinergic activation of NB projections and cortical dysinhibition is sufficient for TC LTP of oEPSCs in the ACx. (e) The diagram of experimental slice preparation depicts that cholinergic afferents from the nucleus basalis are present in the thalamic radiation and can be activated during electrical stimulations of TC LTP.