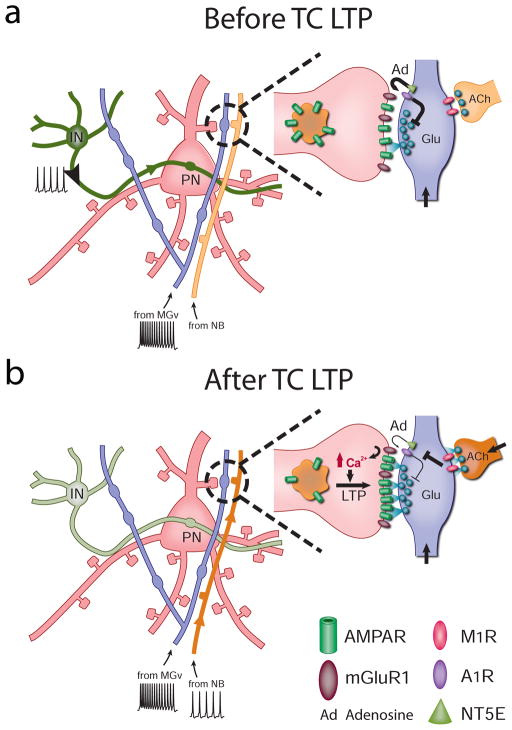
Figure 7. Model of TC LTP.
(a) Active cortical inhibition and inactive cholinergic synapses prevent TC LTP during trains of thalamic stimulations. (b) Cortical deactivation and activation of cholinergic synapses on thalamic projections release the gating of TC LTP in adults. Similar to TC LTD mechanisms, cholinergic activation leads to the downregulation of adenosine (Ad) release from thalamic projections, sustained glutamate (Glu) release at TC synapses, and the induction of postsynaptically expressed mGluR-dependent LTP. Abbreviations: ACh, acetylcholine; IN, cortical inhibitory neuron; MGv, ventral medial geniculate; NB, nucleus basalis; NT5E, ecto-5′-nucleotidase; PN, pyramidal neuron.