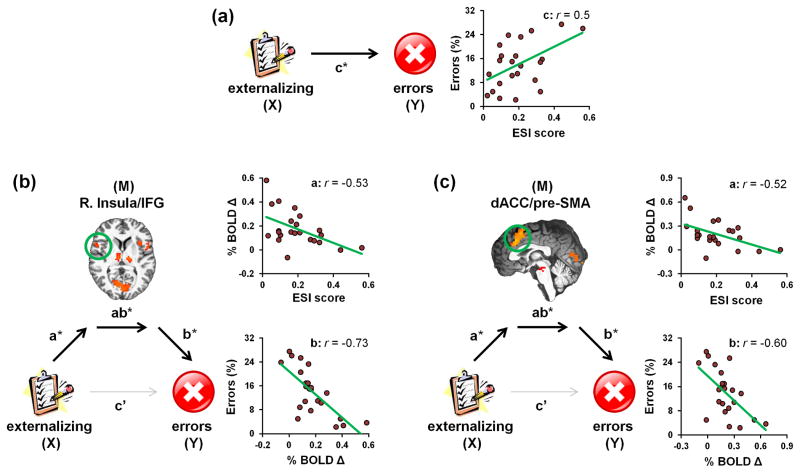
Figure 2.
Mediation models of the association between externalizing tendencies, error rates, and error-related brain activity among acutely abstinent smokers. (a) ESI scores were positively correlated with error rates (i.e., the total effect of X on Y was significant, c path). (b) Error-related right insula activity (M) fully mediated the effect of ESI scores (X) on error rates (Y) as: [1] ESI scores accounted for significant variance in insula activity (a path), [2] insula activity accounted for unique variance in error rates when controlling for ESI scores (b path), [3] the indirect mediation effect was significant (ab path), and [4] ESI’s direct effect on errors was no longer significant when the insula mediator was included in the model (c′ path). (c) Similarly, error-related dACC activity (M) mediated the effect of ESI scores (X) on error rates (Y) when included as the sole mediator in a separate model. See Table 3 for path coefficients. * p < 0.05.