Figure 5.
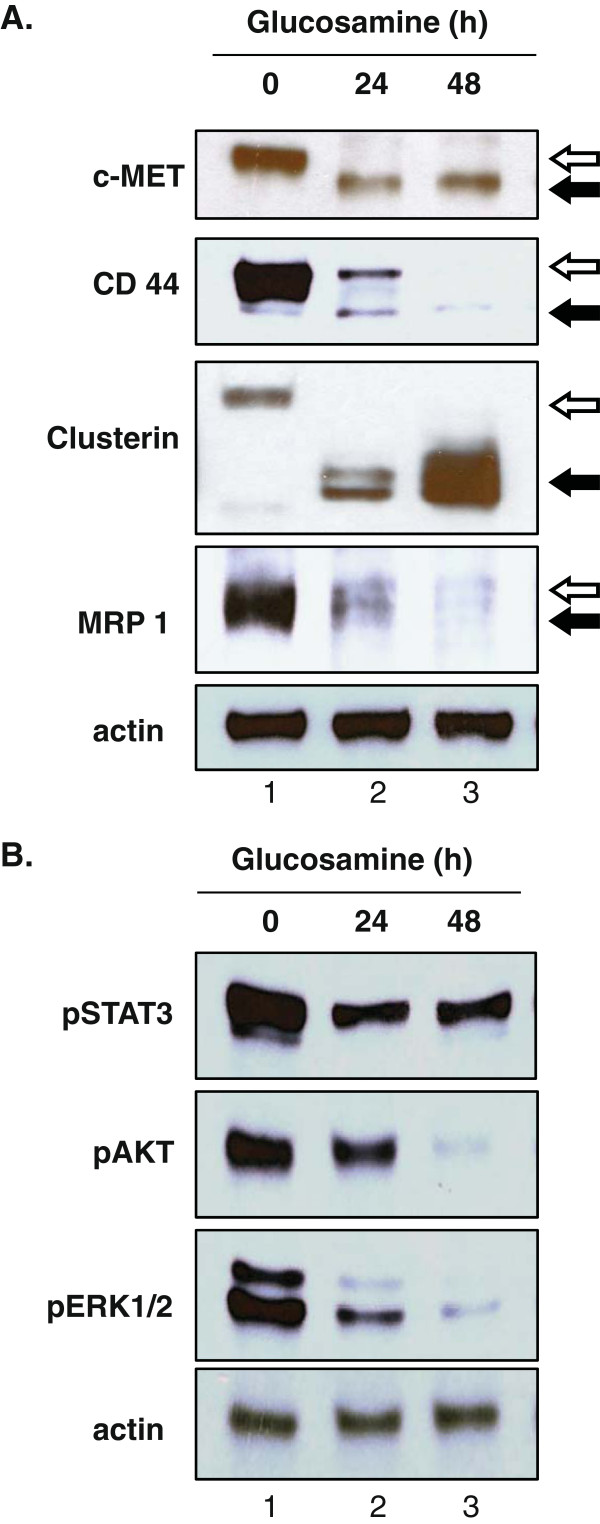
Glucosamine reduced the molecular mass of various glycoproteins by inhibiting N-glycosylation and suppressed the multiple signaling pathways in DU145 cells. (A) Western blot analysis of cells cultured in the presence of 2 mM glucosamine for 24 or 48 h. Whole-cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific for c-MET, CD 44, clusterin, MRP1 and actin (loading control). The open arrow indicates the molecular mass of proteins without glucosamine treatment and the filled arrow indicates the reduced molecular mass of protein following the treatment. (B) Western blot analysis of the phosphorylated (active) STAT, AKT and ERK1/2 proteins after glucosamine treatment. The whole-cell lysates employed in Figure 5A were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific for phospho (Tyr705)-STAT3 (pSTAT3), phospho (Ser473)-AKT (pAKT), phospho (Thr202/Tyr204)-ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) and actin (loading control). Each blot is a representative of three independent experiments.
