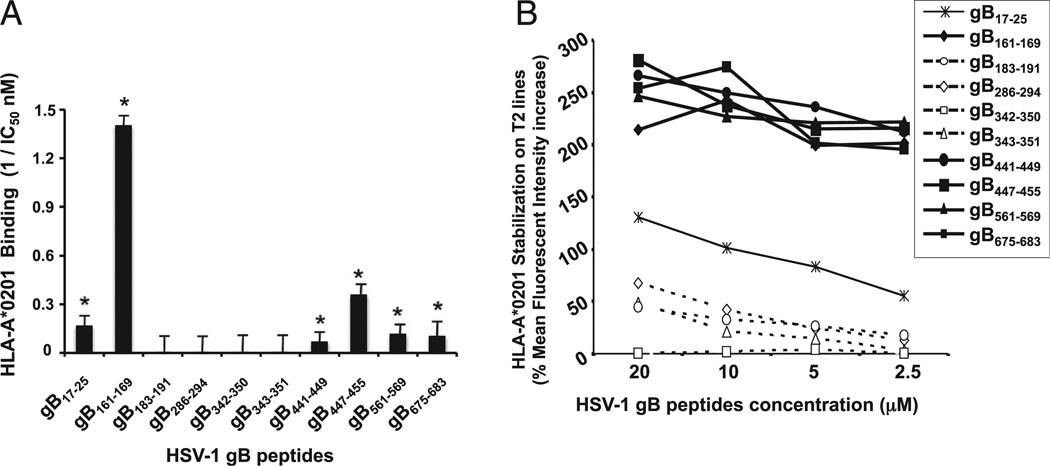
FIGURE 2.
Binding capacities of HSV-1 gB-derived epitope peptides to HLA-A*0201 molecules. (A) In vitro binding capacities of HSV-1 gB-derived epitope peptides to soluble HLA-A*0201 molecules. HSV-1 gB-derived peptides were tested by an ELISA binding assay specific for HLA-A*0201 molecules as described in Materials and Methods. A reference nonherpes peptide was used to validate each assay. Data are expressed as relative activity (ratio of the IC50 of the test peptide to the IC50 of the reference peptide) and are the means of two experiments. Six peptide epitopes with high-affinity binding to HLA-A*0201 molecules (IC50 < 100) are indicated by an asterisk. The columns show four peptide epitopes that failed to bind HLA-A*0201 molecules. (B) Stabilization of HLA-A*02:01 molecules on the surface of T2 cells by gB peptides. T2 cells (3 × 105) were incubated with individual gB peptides at various concentrations (20, 10, 5, and 2.5 µM), as described in Materials and Methods. T2 cells were then stained with FITC-conjugated anti–HLA-A2 mAb (BB7.2). The graph represents the percentage of MFI of HLA-A*02:01 molecules on the surface of T2 cells following incubation with peptides. MFI was calculated as follows: percentage of MFI increase = [(MFI with the given peptide − MFI without peptide)/(MFI without peptide)] × 100. Error bars show SD for three independent experiments. Solid lines represent high levels of HLA-A*02:01 expression on the surface of T2 cells incubated with gB peptides. Broken lines represent low levels of stabilized HLA-A*02:01 expression.