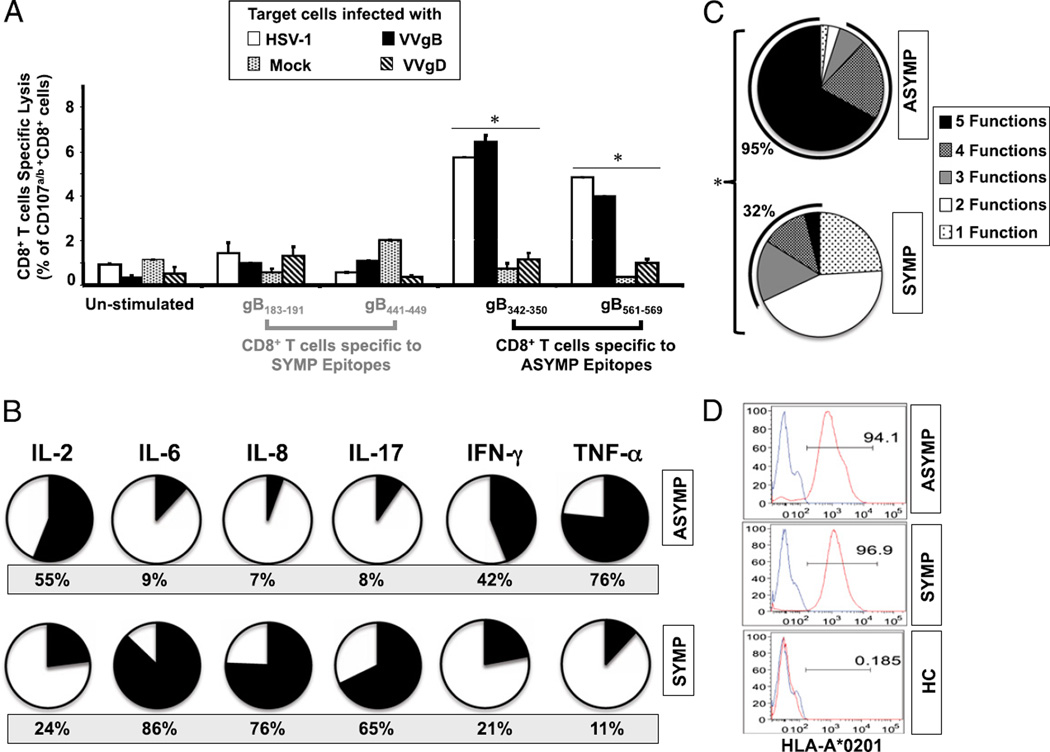
FIGURE 5.
Asymptomatic epitopes preferentially induced polyfunctional CD8+ T cells. (A) ASYMP gB epitope-primed CD8+ T cells displayed lytic activity. CD8+ T cell lines specific to gB342–350 and gB561–569, gB183–191 and gB441–449 epitopes were derived from HLA-A*02:01–positive ASYMP (n = 5) and SYMP (n = 5) individuals. Each CD8+ T cell line was incubated with HSV-1– or VVgB-infected autologous target monocyte-derived dendritic cells (moDCs) in the presence of anti-CD28/49d, FITC-conjugated anti-CD107a and CD107b, and GolgiStop for 6 h. Uninfected target cells were used as control. FACS was used to analyze CD107 expression, as described in Materials and Methods. The graph represents the means ± SD of the percentage of CD107a/b and CD8+ T cells in the presence of uninfected (mock)-, HSV-1–, VVgB-, or control VVgD-infected target cells (moDCs). Samples were acquired on a BD LSR II, and data analysis was performed using FlowJo. *p < 0.005, comparing ASYMP to SYMP individuals using one-way ANOVA test. (B) Summary pie charts showing the average amount of each cytokine produced by CD8+ T cells from ASYMP patients (n = 10, top row) and SYMP patients (n = 8, bottom row), as detected by Luminex assay. The average frequency of different cytokines producing CD8+ T cells is shown under each pie chart. (C) Each pie chart represents the overall mean of CD8+ T cell functions from five HLA-A*02:01–positive ASYMP and five SYMP individuals in responses to stimulation with either SYMP or ASYMP gB peptides. Each sector of the pie chart represents the number of CD8+ T cell functions produced. (D) Representative data showing the expression of HLA-A0201 molecule by dendritic cells from an HLA-A*02:01–positive, HSV-1–seropositive SYMP individual versus an ASYMP individual and by dendritic cells from an HLA-A*02:01–negative, HSV-1–seronegative healthy control (HC).