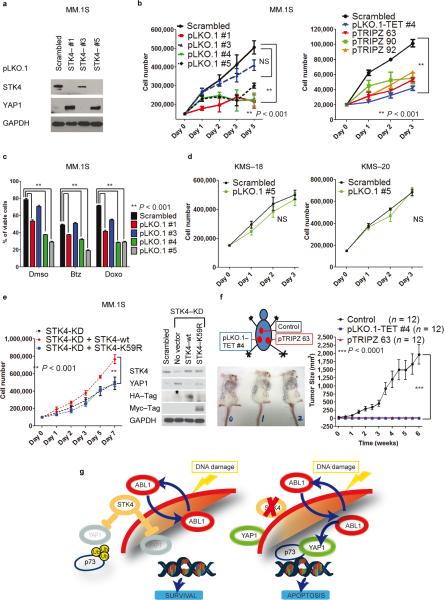
Fig. 5. STK4 knock–down triggers YAP1 re-expression, reducing MM cell proliferation and increasing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
(a) STK4 silencing using lentiviral vector pLKO.1 (after 48h 2μg mL−1 puromycin selection) in MM.1S cells. Western blot for YAP1 and STK4 in STK4–silenced cells (3 representative shRNAs).
(b) Cell number evaluated by cell counting with trypan blue exclusion in MM.1S cells silenced for STK4. Left panel, pLKO.1 lentivectors; right panel, inducible pTRIPZ lentivectors. One representative experiment of three is shown. Data are mean values ± SD of triplicates, Student's t test.
(c) Combined effects of STK4 knock–down associated with treatment with various compounds. Apoptosis evaluated with Annexin V–FITC/PI staining in stably infected cells after 48h incubation with 5 nM bortezomib (Btz) and 40 nM doxorubicin (Doxo).
(d) STK4 silencing by transfection using pLKO.1 scrambled or shRNA #5 vectors. Cell counting as in (b).
(e) MM.1S cells, infected with inducible STK4–shRNAs, after 24 h of 2 μg mL−1 doxycycline were transfected by electroporation with pJ3H–STK4–wild type or pJ3H–STK4–K59R mutant. Left panel: Cell number evaluated as in (b). Right panel: Western blot after 48h transfection.
(f) In vivo evaluation of the effects of STK4 knock–down on MM cells. Left panel: injection scheme and tumor size in three representative mice. Right panel: Growth curve assessing tumor size after injection of MM.1S cells transduced with STK4–specific shRNAs or scrambled–control vectors. Data are mean values ± SD of triplicates, Student's t test.
(g) Proposed model for the ABL1/YAP1/p73 axis and effects of STK4 inhibition on YAP1 levels in MM.