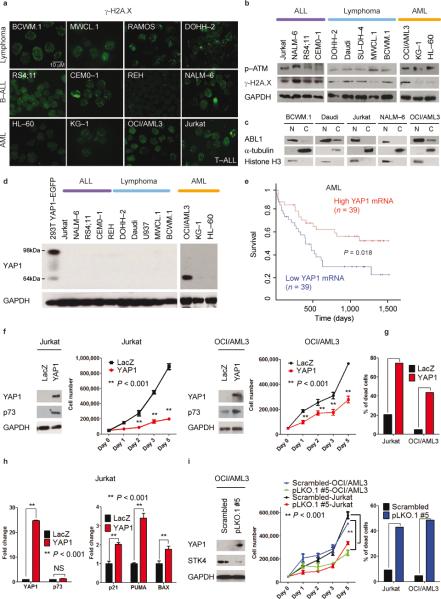
Fig. 6. Lymphoma, leukemia and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia cells present ongoing DNA damage and ABL1 nuclear localization, and undergo apoptosis following STK4-mediated YAP1 increased levels.
(a) γ-H2A.X staining of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (BCWM.1 and MWCL.1), lymphoma (DOHH–2 and RAMOS), B–cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia–B–ALL (RS4;11, CEMO–1, REH, and NALM–6), acute myeloid leukemia–AML (OCI/AML3, KG–1, and HL–60), and T– cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia–T–ALL (Jurkat) cell lines.
(b) Western blot analysis for γ-H2A.X and p–ATM.
(c) Cell lysates from cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions analyzed by Western blot for ABL1 expression. γ-tubulin and Histone H3 were used as loading controls for C and N fractions, respectively.
(d) YAP1 protein expression in ALL, lymphomas, and AML. As positive control, lysates from 293T cells transfected with YAP1–EGFP vector were used (98 kDa–band).
(e) Survival curve relative to YAP1 expression in subjects with AML, obtained from www.canevolve.org, based on GSE12417.
(f) Western blot analysis at 72 h after transfection. Cell number evaluated with cell counting using trypan blue exclusion. Mean values ± SD of triplicate of two experiments are shown. Data are mean values ± SD of triplicates, Student's t test.
(g) Apoptosis evaluated by Annexin V–PE/7–AAD staining after gating on GFP–positive cells.
(h) mRNA levels of YAP1, p73, and p73–target genes (BAX, PUMA, p21).
(i) STK4 knockdown in OCI/AML3 and Jurkat cell lines. Left panel: Western blot for YAP1 and STK4. Middle panel: Cell number measured as in (f) after transfection with scrambled or pLKO.1 #5 vectors. Right panel: Apoptosis by Annexin V–PE/7–AAD staining.