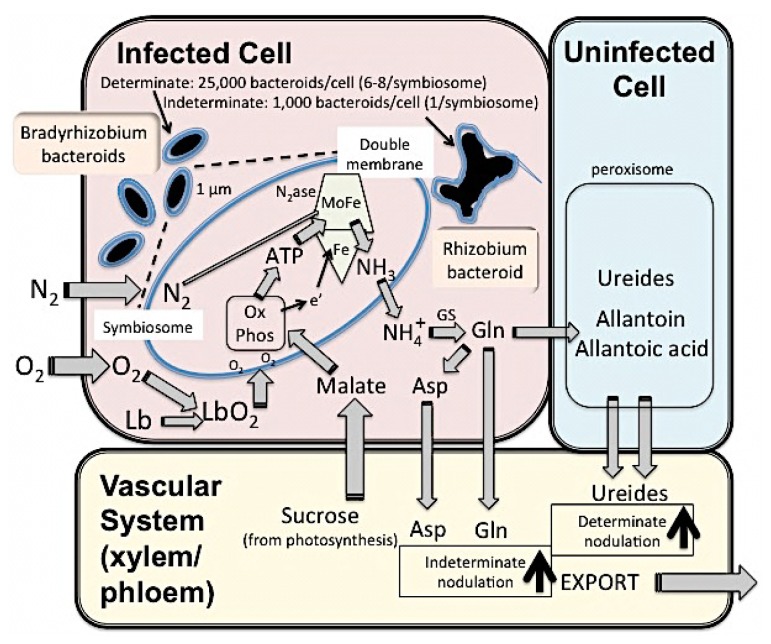
Figure 3.
Schematic mechanisms of symbiotic nitrogen fixation in a legume nodule. N2 entering the symbiosome is converted to NH4+ by the nitrogenase enzyme complex of the bacteria using ATP and an electron donor. The NH4+ is then converted to glutamine via glutamine synthase (GS) and asparagine. Glutamine is exported from the infected cell to uninfected cells where in the peroxisomes ureides, such as allantoin and allantoic acid are synthesised. All the nitrogen transport molecules (Gln, Asp, ureides) are exported to and transported via the vascular system to the rest of the plant. Note that indeterminate and determinate differ in their spectrum of transport molecules. Ureides are highly beneficial as their have a 1:1 carbon:nitrogen ratio (compared to 2:1 for glutamine and asparagine).