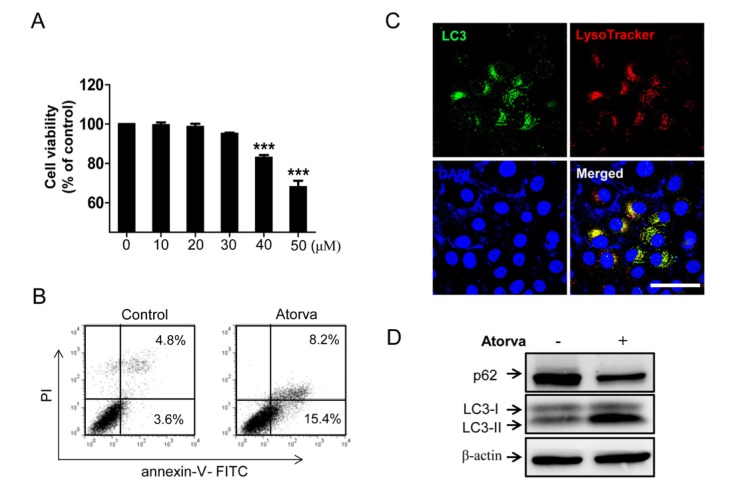
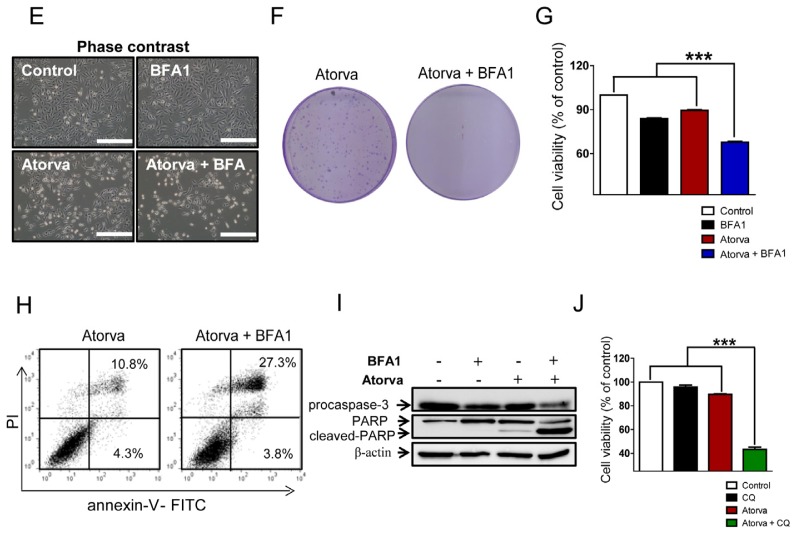
Figure 4.
Inhibition of autophagy induced by atorvastatin improves atorvastatin-induced apoptosis in J82 bladder cancer cells. (A) The cell viability assay to examine the cytotoxic effects of atorvastatin in J82 cells. Differing concentrations of atorvastatin (zero, 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 μM) were administrated over 48 h. The values of cell viability are represented by the mean percent of control ± SEM (n = 3, *** p < 0.001); (B) Evaluation of apoptotic cell death after treatments with 30 μM of atorvastatin by flow cytometry analysis with FITC-conjugated annexin-V and PI staining. Relative proportions of both early and late apoptosis are indicated in right lower and right upper quadrant, respectively in each treatment group; (C) Immunocytochemistry for the co-localization of LC3 puncta (green) and Lysotracker (red, demarcation for the lysosome) in J82 cells after atorvastatin treatments (30 μM) for 24 h. DAPI was used for nucleus staining. Scale bar = 100 μm; (D) Western blot analysis of autophagosome formation markers p62/SQSTM1, LC3-I and LC3-II in untreated (control) and atorvastatin (30 μM) treated J82 cells; (E) Phase contrast images of untreated J82 cells (control), treated J82 cells with 20 μM of bafilomycin A1 (BFA1), 20 μM of atorvastatin (Atorva) and both these agents (Atorva + BFA1). Scale bar = 200 μm; (F) The clonogenic assay to compare the in vitro cell survival potential after treatment with 20 μM of atorvastatin and combined treatment with 20 μM of atorvastatin and BFA1 for 12 days. The colony is defined as containing at least 50 individual cells. Photographs represent each experimental group stained with the clonogenic assay kit; (G) The cell viability assay to examine the cytotoxic effects of 20 μM of BFA1, 20 μM of atorvastatin and both these agents. The values of cell viability are represented by the mean percent of control ± SEM (n = 3, *** p < 0.001); (H) Flow cytometry analysis with FITC-conjugated annexin-V and PI staining to evaluate apoptotic cell death in J82 cells treated with 20 μM of atorvastatin and both 20 μM of BFA1 and atorvastatin for 48 h. Relative proportions of both early and late apoptosis are indicated in right lower and right upper quadrant, respectively in each treatment group; (I) Western blot analysis of apoptotic markers procaspase-3, total PARP and cleaved-PARP in J82 cells treated with 20 μM of BFA1, 20 μM of atorvastatin and both these agents for 48 h; (J) Cell viability assay to compare the cytotoxic effects in J82 cells treated with 20 μM of CQ, 20 μM of atorvastatin and both agents. The values of cell viability are represented by the mean percent of control ± SEM (n = 3, *** p < 0.001).