Figure 1.
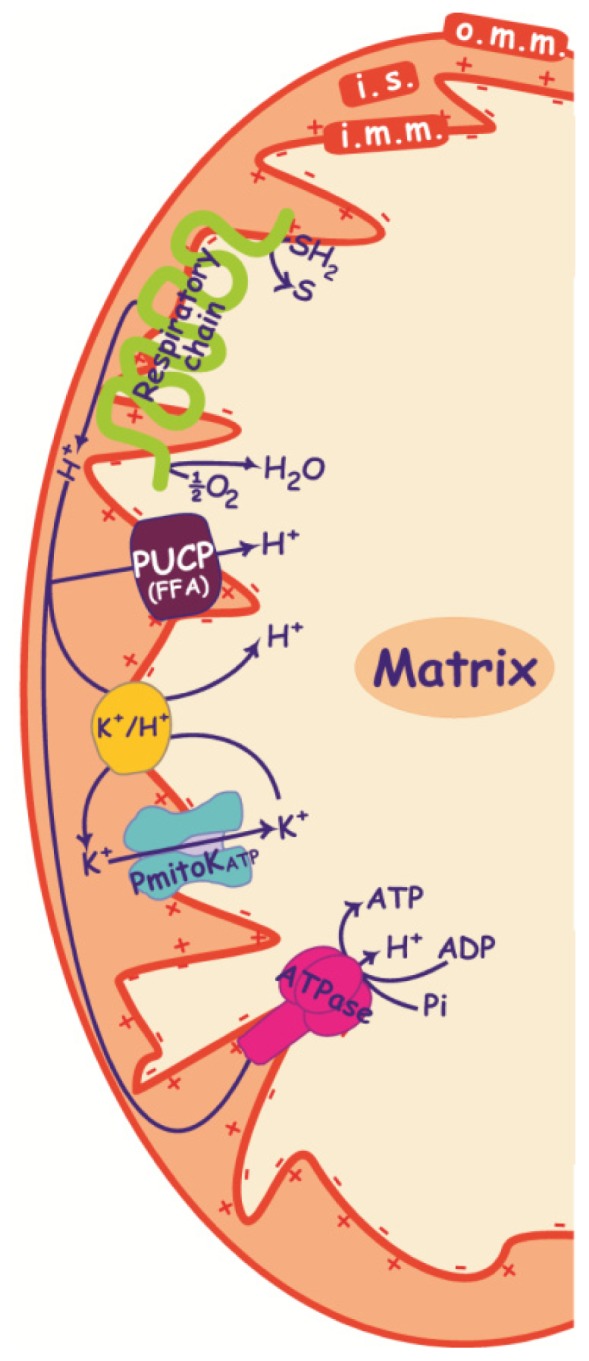
PmitoKATP and PUCP functioning in DWM. Proton ejection into the intermembrane space by the respiratory chain, which generates a proton electrochemical gradient, is indicated. This proton motive force (pmf) consists of two components: the electrical membrane potential or ΔΨ (+ and − signs in the figure), which is the main component of pmf in plant mitochondria, and the proton gradient or ΔpH, which is even negligible in DWM. The proton re-entry into the matrix via the ATPase drives the ATP synthesis. PmitoKATP catalyses the electrophoretic K+ uptake across the inner membrane towards the matrix; when K+ uptake via PmitoKATP is associated with a K+ efflux through the K+/H+ antiporter, a very active K+ cycle is generated, that allows proton re-entry into the matrix. PUCP mediates proton re-entry into the matrix in the presence of free fatty acids (FFAs). SH2, reduced substrates; S, oxidized substrates; i.m.m., inner mitochondrial membrane; i.s., intermembrane space; o.m.m., outer mitochondrial membrane.
