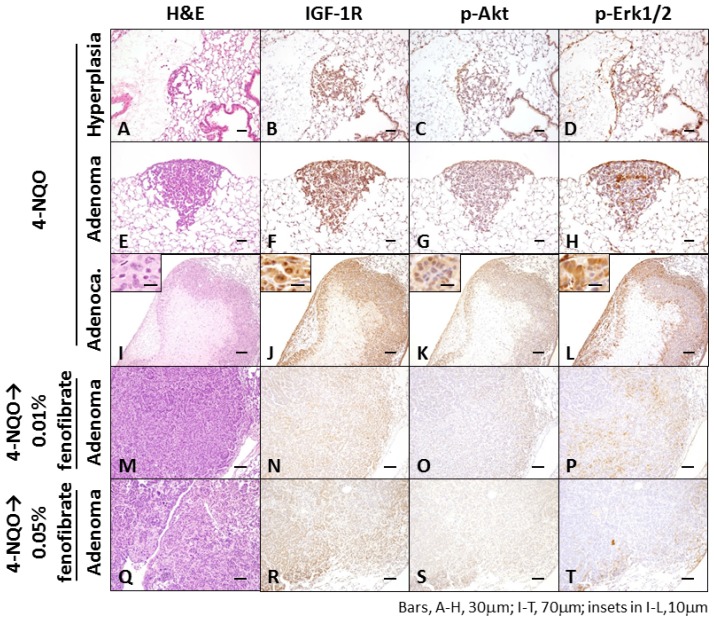
Figure 2.
Histopathology (A,E,I,M,Q) and immunohistochemistry (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), phosphorylated (p)-Akt, and p-extracellular signal-related kinase (Erk) 1/2) of bronchioloalveolar hyperplasia (B–D,N,O,P,R–T), adenoma (F–H), and adenocarcinoma (J–L) induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO) administration in Tsumura Suzuki Obese Diabetic (TSOD) mice. The adenomas M–P and Q–T are developed in a mouse treated with 4-NQO followed by dietary exposure to 0.01% and 0.05% fenofibrate, respectively. Alveolar hyperplasia (A–D), adenoma (E–H), and adenocarcinoma (I–L) were positively stained with IGF-1R (B,F,J), p-Akt (C,G,K), and p-Erk1/2 (D,H,L) antibodies, respectively. Note the weakly positive or negative reactions against IGF-1R, p-Akt, and p-Erk1/2 of adenoma in mice that received 4-NQO and fenofibrate. (A,E,I,M,Q): H&E stain; (B,F,J,N,R): IGF-1R immunohistochemistry; (C,G,K,O,S): p-Akt immunohistochemistry; and (D,H,L,P,T): p-Erk1/2 immunohistochemistry.