Figure 3. Contribution of ERK and AKT pathways to the combined treatment-induced growth inhibition against HepG2 cells.
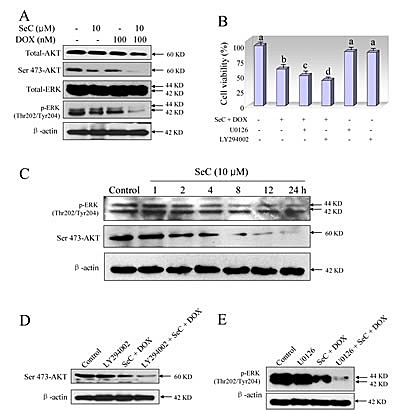
A. SeC synergizes DOX-induced inactivation of ERK and AKT. Protection expression was detected by western blotting method. Briefly, HepG2 cell were pre-treated with 10 μM SeC for 24 h and co-treated with 100 nM DOX for 24 h. Then cells were lysed and total protein were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with specific primary antibodies. Equal loading was affirmed by stripping immunoblots and reprobing for β-actin. B. Inhibitors of ERK (U0126) and AKT (LY294002) enhance combined treatment-induced growth inhibition against HepG2 cells. Cells were pretreated with 10 μM U0126 or 10 μM LY294002 for 1 h before combined treatment with SeC and DOX. Cell viability was detected by MTT assay. C. Time-dependent effects of SeC on expression of p-AKT and p-ERK in HepG2 cells. D. Inhibitors of AKT (LY294002) enhance combined treatment-induced inactivation of AKT. E. Inhibitors of ERK (U0126) enhance combined treatment-induced inactivation of ERK.
