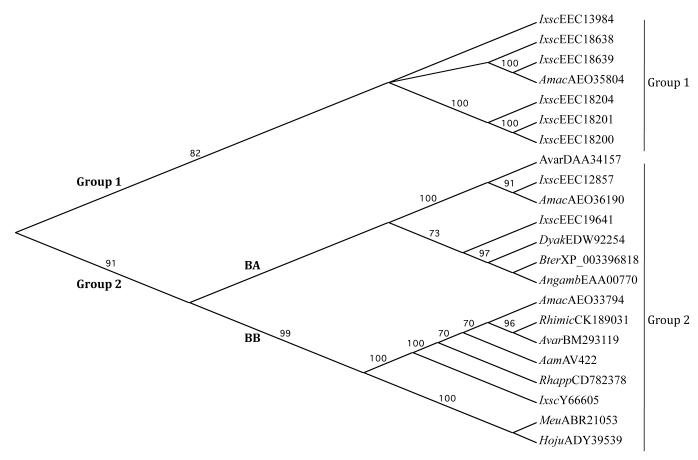
Fig. 3.
Neighbor joining guide phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of Amblyomma americanum AamAv422 putative protein to AamAV422-like proteins from ticks (n = 15) and non-tick arthropods (n = 6). The predicted AamAV422 protein sequence was aligned with AamAV422-like sequences: Rhimic, Rhipicephalus microplus (CK189031); Rhapp, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus (CD782378); Amac, Amblyomma maculatum (AE033794, AE035804, AE036190); Avar, Amblyomma variegatum (DAA34157 and BM293119); Ixsc, Ixodes scapularis (Y66605, EEC1287, EEC13894, EEC18200, EEC18201, EEC18204, EEC18638, EEC18639 and EEC19641); Angamb, Anopheles gambiae (EAA00770); Meu, Mesobuthus eupeus (ABR21053); Hoju, Hottentotta judaica (ADY39539); Bter, Bombus terrestris (XP_003396818) and Dyak, Drosophila yakuba (EDW92254), using ClustalW. The guide phylogenetic tree was developed using the MacVector Neighbor joining method default parameters as described in Section 2.3. Groups 1 and 2, and subgroups BA and BB are indicated. Numbers on each branch represent bootstrap values that signify the level of confidence in the branch.