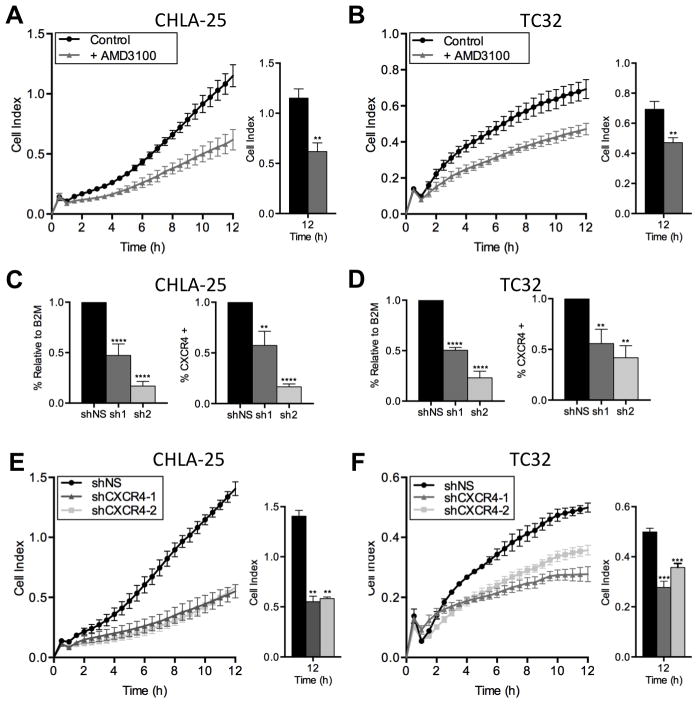
Figure 4. CXCR4 promotes chemotactic migration of Ewing sarcoma cells.
A & B. Migration of CHLA-25 (A) and TC32 (B) cells towards SDF-1α (100ng/mL) was measured using real-time cell analysis (xCELLigence CIM-Plate 16) in the presence and absence of the CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100. AMD3100 significantly inhibited chemotaxis.
C & D. Knockdown of CXCR4 was effectively achieved in CHLA-25 (C) and TC32 cells (D) using lentiviral transduction of 2 different shRNA sequences directed against CXCR4 (sh1 and sh2). Control cells were transduced with an inert non-silencing shRNA vector (shNS). Successful knockdown was confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR (left panels) and flow cytometry (right panels
E & F. Migration of CHLA-25 (E) and TC32 (F) cells towards SDF-1α (100ng/mL) was inhibited following knockdown of CXCR4.
In all panels, graphs represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments with four replicates per condition. **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001 and ****, P < 0.0001 as compared to controls.