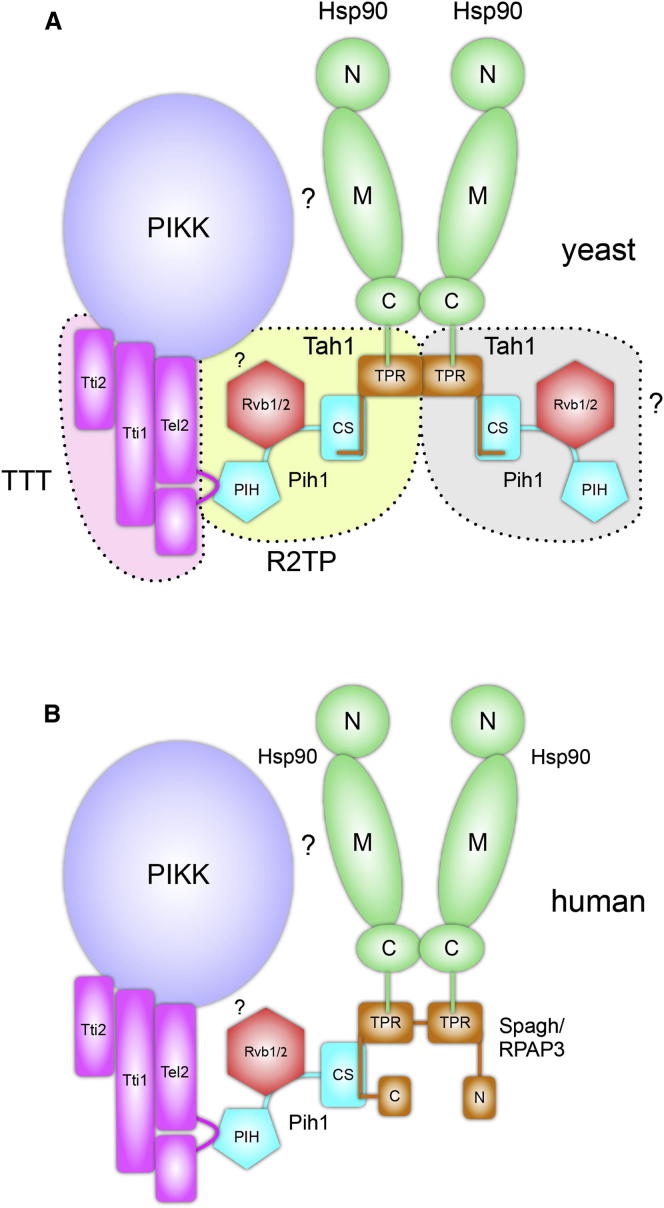
Figure 7.
Assembly of the Hsp90-R2TP-TTT Supercomplex
(A) Structure of the overall yeast Hsp90-R2TP-TTT supercomplex required for activation of PIKK enzymes such as TOR. The data presented here provide detailed insights into the chain of protein-protein interactions connecting the C terminus of Hsp90 to the TPR domain of Tah1, the C-terminal segment of Tah1 to the CS-domain of Pih1, and the PIH-domain of Pih1 to the CK2 sites on Tel2. Whether Rvb1/2 and Hsp90 directly contact the client PIKK remains to be determined. Tah1 binds Hsp90 as a dimer, occupying both TPR-binding sites on an Hsp90 dimer. However, whether this causes recruitment of a second Pih1-complex and potentially an additional TTT-PIKK complex is unknown.
(B) As in (A), but for the metazoan system where Tah1 function is replaced by Spagh/RPAP3, which binds both TPR-binding sites on an Hsp90 dimer as a single polypeptide. The role of the additional N- and C-terminal domains of Spagh/RPAP3 in PIKK activation remains to be determined.