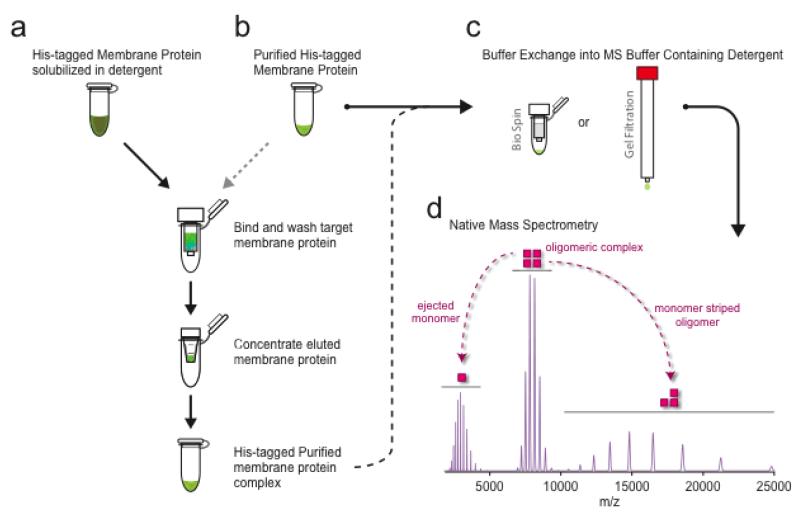
Figure 1. An overview of a typical membrane protein purification and preparation, and analysis by mass spectrometry of the intact complex.
(a) Purified membranes containing over-expressed membrane protein fused to green fluorescent protein (GFP) and His-tag is solubilized in a detergent of interest. Solubilized membrane protein is purified using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) and concentrated prior to preparation for native mass spectrometry (MS). (b) Detergent can be screened or optimized starting with a purified membrane protein and follow the procedure outlined above to exchange into a different detergent. Furthermore, membrane proteins can be prepared from solubilized membranes in different detergents followed by purification using IMAC. (c) Purified membrane proteins are buffer exchanged into an MS-compatible buffer containing two times the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of the detergent of interest. Typically buffer exchange centrifugal devices, such as a Bio Spin device, are used. Alternatively, buffer exchange can also be achieved using a small analytical gel filtration column. (d) Theoretical mass spectrum for a tetrameric membrane protein complex (200 kDa) with a protein monomeric mass of 50 kDa. Under MS conditions, the oligomeric or tetrameric complex, centered around 8,500 m/z, undergoes collisional induced disassociation. Activation results in the ejection of a highly charged monomer, centered around 3,500 m/z, and a monomer stripped oligomer or oligomeric complex minus the ejected monomer, spanning the region 10,000 to 25,000 m/z.