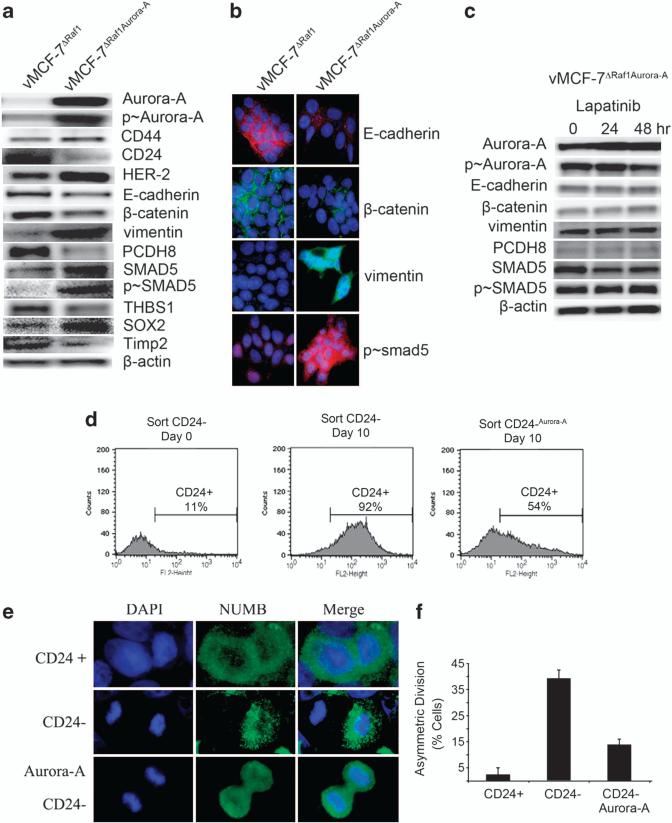
Figure 3.
Overexpression of Aurora-A induces EMT and a cancer stem cell-like phenotype. (a) Immunoblot analysis of vMCF-7ΔRaf-1 and vMCF-7ΔRaf-1 cells engineered to overexpress Aurora-A (vMCF-7ΔRaf-1/Aurora-A) showing that vMCF-7ΔRaf-1/Aurora-A cells overexpress CD44, HER-2/Neu and Aurora-A, CD24 downregulation, and expression of EMT and cancer stem cell markers. (b) Immunofluorescence analysis of vMCF-7ΔRaf-1 and vMCF-7ΔRaf-1/Aurora-A cells showing activation of EMT in vMCF-7ΔRaf-1/Aurora-A cells characterized by loss of E-cadherin and β-catenin, expression of vimentin and nuclear localization of p-SMAD5. (c) Immunoblot analysis of vMCF-7ΔRaf-1/Aurora-A cells treated with 1 μM lapatinib showing that constitutive activation of Aurora-A kinase activity is essential for the development of EMT regardless inhibition of HER-2/Neu signaling. (d) FACS analysis showing that sorted CD24–/low cells infected with a lentivector overexpressing Aurora-A maintain a higher percentage of cells carrying a CD24–/low phenotype after 10 days in culture compared with control CD24–/low cells that give rise to a CD24+ subpopulation. (e) Asymmetric division in CD24–/low cells, and symmetric division in CD24+ and CD24–/low cells overexpressing Aurora-A (CD24–/low/Aurora-A). The marker of asymmetric mitotic divisions NUMB was labeled in green and DNA was labeled in blue with Hoechst dye. (f) Graph showing the percentage of cells with asymmetric divisions in CD24+, CD24–/low and CD24–/low/Aurora-A cells from three independent experiments (±s.d.).