Figure 3.
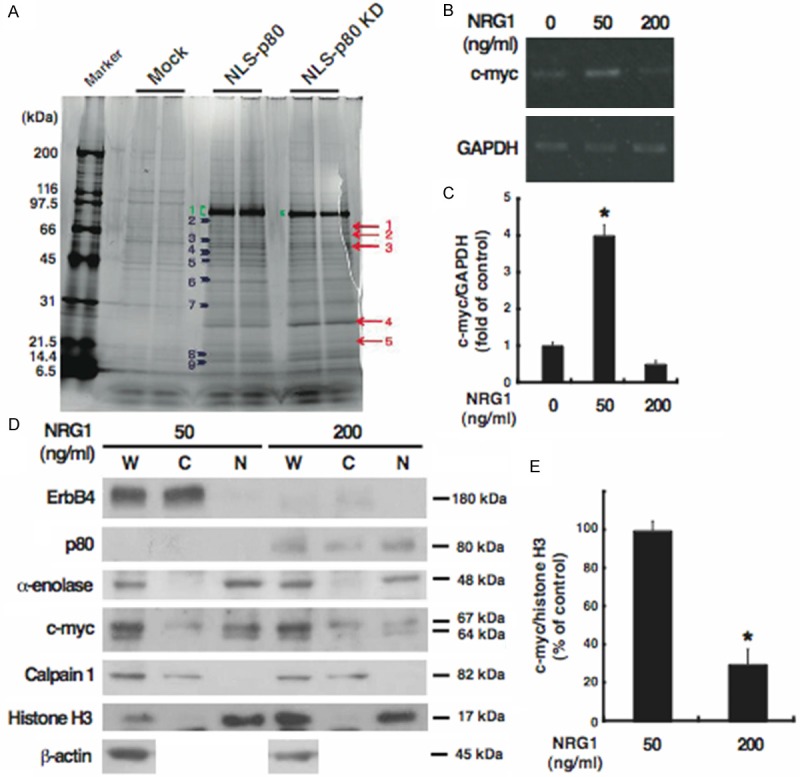
Identification and subcellular distribution of α-enolase as a novel p80-binding protein. A: Cells were transfected with each of the expression plasmids for NLS-p80 and NLS-p80 KD, or the empty vector (Mock), and subjected to immunoprecipitation with p80. Coimmunoprecipitates were loaded onto SDS-PAGE gels and stained by Oriole Fluorescent Gel Stain, followed by proteomics. Proteins detected in both of the cells overexpressing NLS-p80 or NLS-p80 KD but not in the control cells are indicated by arrows; proteins detected more strongly in both of the cells overexpressing NLS-p80 or NLS-p80 KD than in the control cells are indicated by arrowheads; NLS-p80 and NLS-p80 KD are indicated by parentheses. A protein of the band No. 4, indicated by an arrowhead, is α-enolase. B and C: Total RNA was extracted from cells treated for 24 h without (0) or with each of 50 and 200 ng/ml NRG1 and analyzed by RT-PCR for c-myc (338 bp) and GAPDH (212 bp) as the internal control. Results were representative of three independent experiments (B) and quantified by densitometry as a fold (mean ± S.E.) of c-myc expression, normalized to GAPDH expression, in cells treated with NRG1, relative to c-myc expression in untreated cells (C). D and E: Whole extracts (W) and the cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions were prepared from cells treated for 24 h with 50 or 200 ng/ml NRG1 and analyzed by Western blotting for the indicated proteins. For c-myc, the alternative translation initiations from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site result in the production of two isoforms with distinct amino-termini (67 and 64 kDa) [41]. Results were representative of three independent experiments (D) and quantified by densitometry as a percentage (mean ± S.E.) of c-myc amounts (the sum of the 67-kDa and 64-kDa protein), normalized to histone H3 amounts, in the nuclear fraction derived from cells treated with NRG1, relative to c-myc amounts in the nuclear fraction derived from untreated cells (E). *, p < 0.05.
