Figure 2.
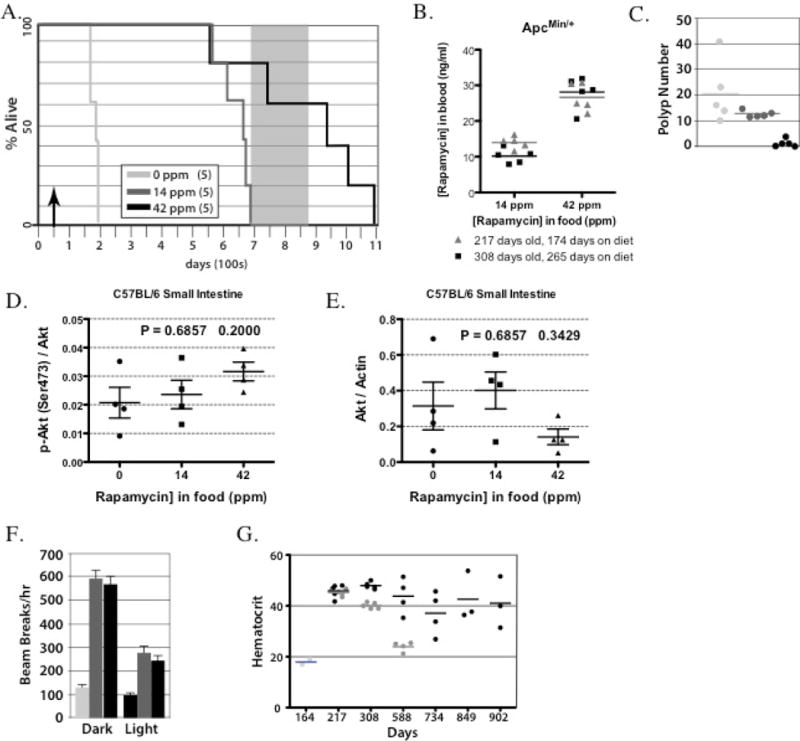
eRapa increases life and health span for ApcMin/+ mice. (A) eRapa increases life span for ApcMin/+ mice. The grey box represents a range of median life spans for C57BL/6J female mice taken from previous studies {Wijnhoven et al., 2005, #5122; Yuan et al., 2009, #78681; Zhang et al., 2013, #44400}, which is also representative of syngeneic colonies at the Barshop Institute animal facility used in our study. Note that 60% of the 42 ppm eRapa fed ApcMin/+ mice have lived beyond this range. (B) Rapamycin blood levels in ApcMin/+ mice at 217 days (174 days on eRapa diets, which averaged 14 ng/ml or 26.6 ng/ml on 14 ppm or 42 ppm diets, respectively) or at 308 days of age (265 days on eRapa diet, which averaged 10.2 ng/ml or 28.1 ng/ml on 14 ppm or 42 ppm diets, respectively) (C) Polyp count for ApcMin/+ mice at the time of death. Note the first and third mouse that died from the 42 ppm cohort had no polyps. (D&E) Graph showing quantification of phosphorylation state-dependent signal P(Ser473)Akt to phosphorylation state-independent signal (D) and Akt to actin antibody signal (E). (F) eRapa improves physical activity in ApcMin/+ mice. Graphed is the mean number of beam breaks (activity) for light (=inactive) and dark (=active) phases of the day. The food area of the cage is excluded. (G) eRapa maintains normal hematocrits in ApcMin/+ mice. Note the dose response. Also note the normal hematocrit as compared to wild type C57Bl/6 mice (~40%) in the high dose group even at late time points when many wild type C57Bl/6 mice would die from natural causes.
