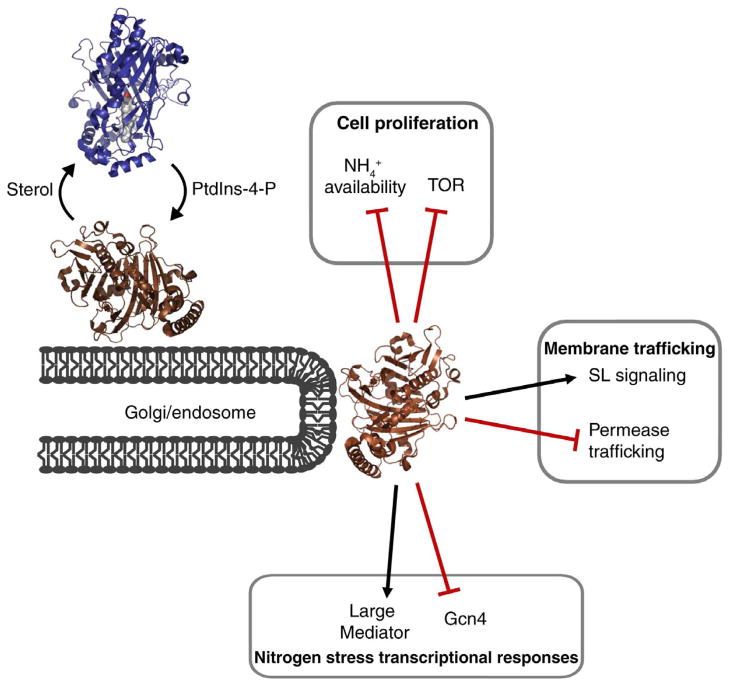
Figure 2. Kes1 integrates PtdIns-4-P signaling, sterols, TGN trafficking control, and larger cellular physiological responses.
Kes1 is recruited to Golgi membranes by virtue of its ability to bind PtdIns-4-P where it clamps availability of this phosphoinositide and functions as a trafficking ‘brake’ [62]. Sterol binding at the TGN releases Kes1 from the membrane, thereby releasing the trafficking brake. Larger consequences of this negative regulation of membrane trafficking include TGN/endosomal sphingolipid metabolism-mediated control of cell proliferation, TOR signaling, and execution of nitrogen stress transcriptional responses.