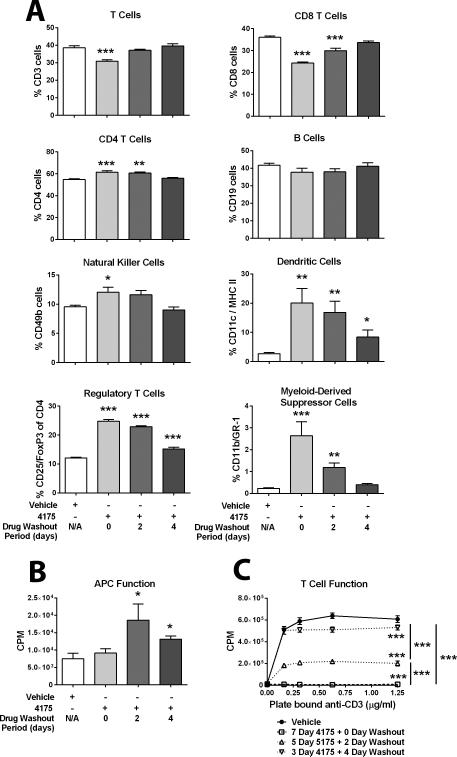
Figure 3. Effect of ARI-4175 on splenic immune-cell subsets and function.
Female C57BL/6 mice were given ARI-4175 (200 μg/mouse/day) by gavage for either 3 days (followed by 4 days of vehicle), 5 days (followed by 2 days of vehicle), or 7 days (followed by 0 days of vehicle). Control mice received vehicle for 7 days. A. ARI-4175 has varied effects on immune-cell subsets. On day 7, the percent of indicated immune-cell populations in individual mice (n = 3–5) was determined by flow cytometric analysis with the indicated markers. Data are representative of one experiment and are presented as mean ± SEM. B. ARI-4175 enhanced allostimulatory (H-2b vs. H-2d) activity. On day 7, splenocytes from ARI-4175-treated female C57BL/6 mice (effector cells) were cocultured with splenocytes from untreated Balb/c mice (target cells) for 4 days at an effector:stimulator ratio of 1:1 to 32:1. [3H]Thymidine was added during the final 18 h and incorporation was measured. Data shown represent an effector:stimulator ratio of 1:1 and mean ± SEM for triplicate wells. C. ARI-4175 reduced T-cell function. On day 7, splenocytes from ARI-4175-treated female C57BL/6 mice were incubated in the presence of increasing concentrations of plate-bound anti-CD3 for 3 days. [3H]Thymidine was added during the final 18 h and incorporation was measured. Data represent mean ± SEM for triplicate wells. Asterisks denote statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) relative to vehicle-treated mice.