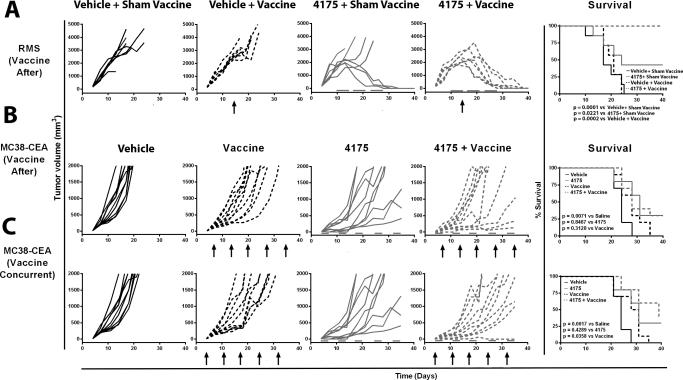
Figure 4. ARI-4175 given in combination with vaccine decreased tumor volume and improved survival in M3-9-M and MC38-CEA tumor models.
A. For the M3-9-M model, C57BL/6 mice were implanted on day 0 with 1×106 cells intramuscularly on the flank. Mice were given ARI-4175 (200 μg/mouse/day) or vehicle by gavage 5 times/week on days 10–14, 17–21, and 24–28. On day 14, mice received an intraperitoneal injection of DC-based vaccine (pulsed with irradiated tumor) or sham vaccine (non-pulsed DCs). B. For the MC38-CEA model, where vaccine was administered following ARI-4175, CEA-tg C57BL/6 mice were implanted on day 0 with 3×105 MC38-CEA cells subcutaneously. Mice were given either ARI-4175 (200 μg/mouse/day) or vehicle by gavage 3 days/week on days 4–6, 11–13, 18–20, 25–27, 32–34, and 39–41. Vaccinated mice received a prime of MVA-CEA-TRICOM on day 6 and weekly boosts with rF-CEA-TRICOM. C. For the MC38-CEA model, where vaccine was administered concurrently with ARI-4175, CEA-tg C57BL/6 mice were implanted on day 0 with 3×105 MC38-CEA cells subcutaneously. Mice were given either ARI-4175 (200 μg/mouse/day) or vehicle by gavage 3 times/week on days 4–6, 11–13, 18–20, 25–27, 32–34, and 39–41. Vaccinated mice received a prime with MVA-CEA-TRICOM on day 4 and weekly boosts with rF-CEA-TRICOM. Tumor volume was assessed 2–3 times/week. Statistical analysis of survival based on the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was performed on day 40. Arrows indicate vaccination. Gray bars indicate duration of ARI-4175 treatment.