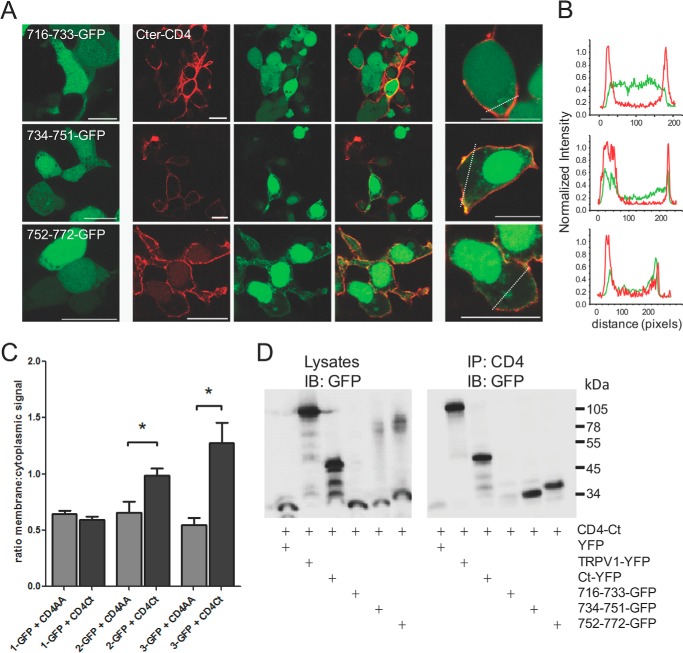
FIGURE 3.
Small TRPV1 C-terminal peptides 734–751 and 752–772 interact with the full-length C terminus. A, the three GFP-tagged fragments of the TRPV1 C terminus were co-expressed in tsA-201 cells with the membrane-tethered CD4-tagged TRPV1 C terminus. Interaction between the peptide and the full-length C terminus results in translocation of the GFP signal to the membrane. Left panel, GFP-tagged peptide alone. Center panels, GFP-tagged peptide (green) co-expressed with CD4-C terminus (red). Right panels, higher magnification images of center panels; all scale bars = 20 μm. B, line scans from cells in the right panel of A indicating that peptides 734–751 and 752–772 are present at the cell membrane with the CD4-C terminus, whereas peptide 716–733 exhibits diffuse distribution within the cell. C, bar chart representing the ratio (mean ± S.E.) of membrane:cytoplasmic signal of GFP-tagged peptides. The 734–751 and 752–772 show membrane translocation when co-expressed with the membrane-tethered CD4-tagged TRPV1 C terminus (CD4Ct, black bars) as compared with CD4-tagged control (CD4AA, gray bars). *, p < 0.05, ANOVA, followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test. n = 6–21 cells per transfection. D, co-immunoprecipitation of GFP-tagged peptides with the full-length CD4-tagged C terminus of TRPV1. 734–751 and 752–772 co-precipitate with CD4-tagged TRPV1 C terminus. Left panel, input lysates immunoblotted (IB) for GFP; right panel, CD4-tagged TRPV1 C terminus immunoprecipitates (IP) the TRPV1 channel, the C terminus, and the 734–751 as well as the 752–772 peptides but not the 716–733 peptide. Transfected tsA cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-CD4 antibody and blotted for GFP. Molecular masses in kDa are indicated on the right. Data are representative of three independent experiments.