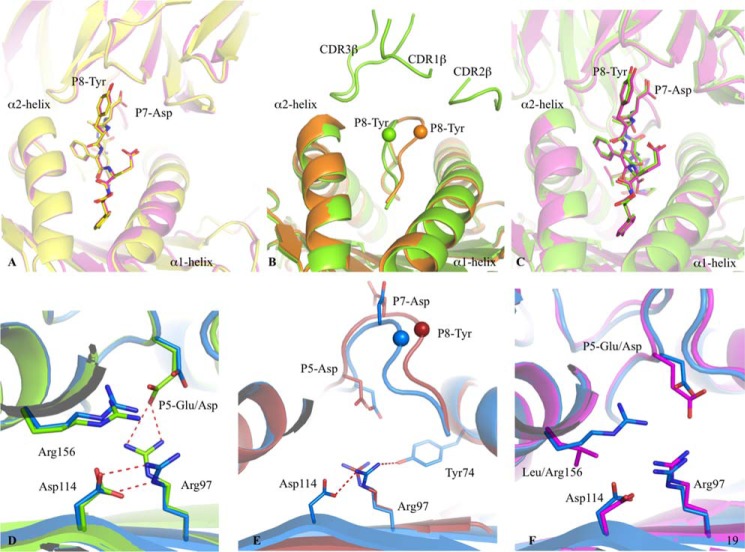
FIGURE 6.
Peptide flexibility enhances the TK3 TCR recognition. A, superposition of the TK3 TCR-HLA-B*35:01-HPVG-Q5 complex (yellow) with the TK3 TCR-HLA-B*35:01-HPVG complex (pink), with the TCR and HLA in schematic format, and the peptide in stick representation. B, superposition of the HLA-B*35:08-HPVG free (orange) and bound to the TK3 TCR (green). The peptide is represented in schematic format with the Cα of the P8-Tyr residue show as a sphere. C, superposition of the TK3 TCR in complex with the HLA-B*35:01-HPVG (pink) and HLA-B*35:08-HPVG (green), with the TCR and HLA in schematic representation and the peptide in stick representation. D, superposition of the HLA-B*35:08-HPVG (green) with HLA-B*35:08-HPVG-D5 (blue) in complex with the TK3 TCR. The red dash lines represent the hydrogen bonds formed between Arg-97, Asp-114, and the P5-Glu. E, superposition of the HLA-B*35:08-HPVG-D5 free (red) and bound to the TK3 TCR (blue). The spheres represent the Cα atom of the P8-Tyr from the HPVG-D65 peptide, the red dashed lines represent the hydrogen bonds formed by Arg-97 with Asp-114 and Tyr-74 in the TK3 TCR-HLA-B*35:08-HPVG-D5 structure. F, superposition of the HLA-B*35:08-HPVG-D5 (blue) and HLA-B*35:01-HPVG (pink) in complex with the TK3 TCR.