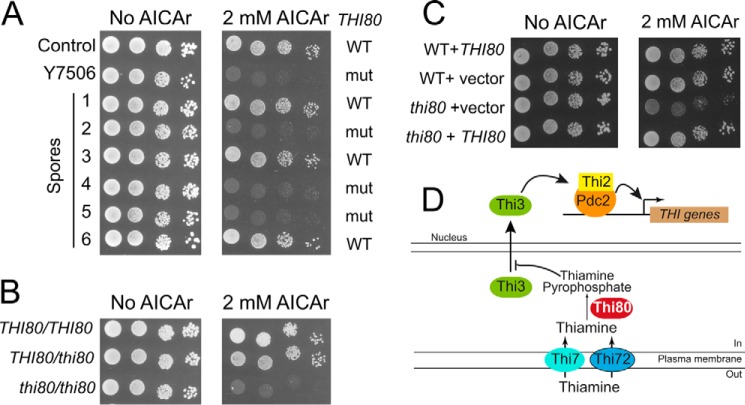
FIGURE 2.
The S90P recessive mutation in the THI80 gene is responsible for AICAr hypersensitivity of the Y7506 mutant strain. A, the thi80 mutation is genetically linked to AICAr sensitivity. The cells were grown overnight, serially diluted, and spotted on SDcasaWAU medium containing external AICAr. Parental strains ade16 ade17 ade8 his1 either mutated (Y7506) or not (control, Y7242) in the THI80 gene, and six derived spores are shown. The plates were imaged after 3 days at 37 °C. WT and mut, respectively, stand for wild-type (THI80) and mutated (thi80) versions of thiamine pyrophosphate kinase gene, as determined by sequencing. B, the thi80 (S90P) mutation leading to AICAr sensitivity is recessive. Diploid ade16 ade17 ade8 his1 strains mutated (thi80) or not (THI80) in thiamine pyrophosphate kinase gene were grown, diluted, and spotted on SDcasaWAU medium as in Fig. 2A. C, complementation by the wild-type THI80 gene. Haploid ade16 ade17 ade8 his1 strains (WT, Y7242; or thi80, Y7506) were transformed with a centromeric plasmid expressing (THI80) or not (vector) a wild-type copy of THI80. Transformants were grown, diluted, and spotted on SDcasaWA medium as in Fig. 2A. In A–C, the plates were imaged after 3 days at 37 °C. D, schematic representation of thiamine metabolism and resulting regulation of THI gene expression.