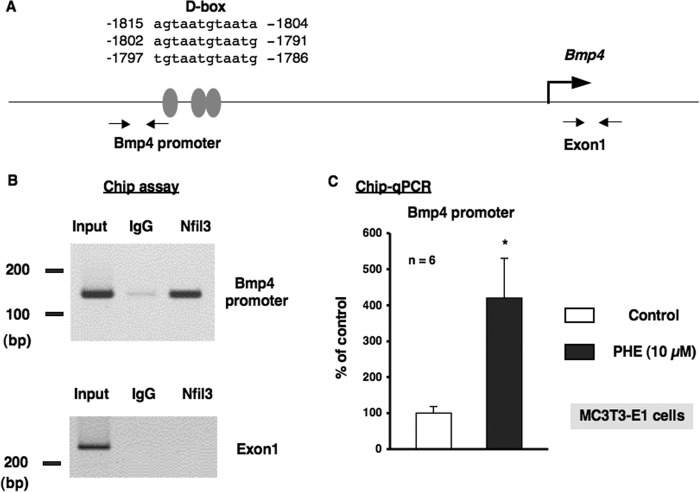
FIGURE 10.
α1-AR signaling regulated the promoter element binding of Nfil3 to the Bmp4 gene in MC3T3-E1 cells. A, schematic showing the three potential binding sites of the proximal D-box in the putative promoter element of the Bmp4 gene. Grey ovals indicate the sites that match consensus D-box element sequences in the mouse Bmp4 gene. PCR was performed using sequences found in the 5′ flanking region (−1906 to −1887 and −1777 to −1758) and the exon 1 region (+243 to +262 and +442 to +461) of the mouse Bmp4 gene as primers. B, ChIP assays with antibodies against Nfil3 from MC3T3-E1 cells. A representative image of ChIP agarose gel electrophoresis. Nfil3/E4BP4 occupancy of this promoter region of the Bmp4 gene was enriched in MC3T3-E1 cells. Chromatin was prepared from MC3T3-E1 cells and immunoprecipitated with anti-Nfil3, followed by PCR using primers from the Bmp4 promoter or exon 1 of the Bmp4 gene as a control. Ten percent of the input was loaded as a control. Anti-IgG antibodies were used as a control for specificity. PCR-amplified bands of the Bmp4 promoter (top panel) and exon 1 of the Bmp4 genes (bottom panel) in chromatin were precipitated by Nfil3 antibodies. IgG, nonimmune rabbit IgG; Nfil3, rabbit Nfil3 antibodies; Input, DNA input. C, PHE increased the promoter element binding of Nfil3/E4BP4 to the Bmp4 gene. ChIP analysis revealed the increased binding of Nfil3 to the binding site of the Bmp4 promoter element in MC3T3-E1 cells following the PHE treatments. Each value represents the mean ± S.E. of six separate experiments. *, p < 0.05, significantly different from the value obtained in MC3T3-E1 cells cultured in the absence of PHE.