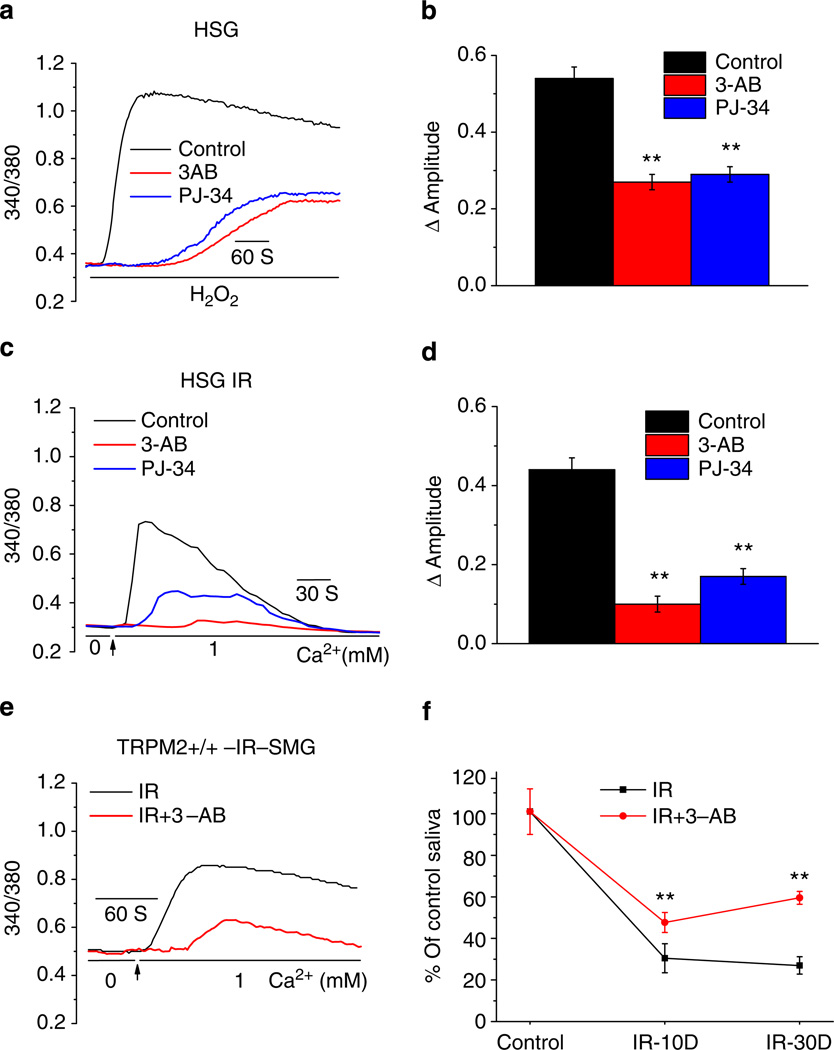
Figure 5. PARP inhibitors attenuate IR-induced TRPM2 activation and loss of saliva flow.
(a,c) Effect of PARP1 inhibitors 3-AB and PJ-34 (10 and 1 µM, respectively) on H2O2- and IR-induced increases in [Ca2+]i in HSG cells. Cells were incubated with agents for 30 min before H2O2 addition or 15 min before IR. Traces are representative data from 225–355 cells. (b,d) Average [Ca2+]i changes (above basal) calculated from the experiments shown in a,c. **Indicates values that are significantly different (P < 0.01, numbers of cells from 265–315) from the respective controls in each case. (e) Constitutive [Ca2+]i increases in acini isolated from submandibular glands that were excised 24 h after 15 Gy IR. (f) Saliva flow was monitored 10 and 30 day after 15 Gy IR of TRPM2+/+ mice (controls or mice treated with 3-AB, 20mg kg−1 body weight, i.p. injection). Salivary secretion is expressed relative to that measured before IR (**indicates a significant difference (P < 0.01) compared with the corresponding values in mice not treated with 3-AB, 10 mice in each group). All values in b,d and f are defined as mean ± s.e.