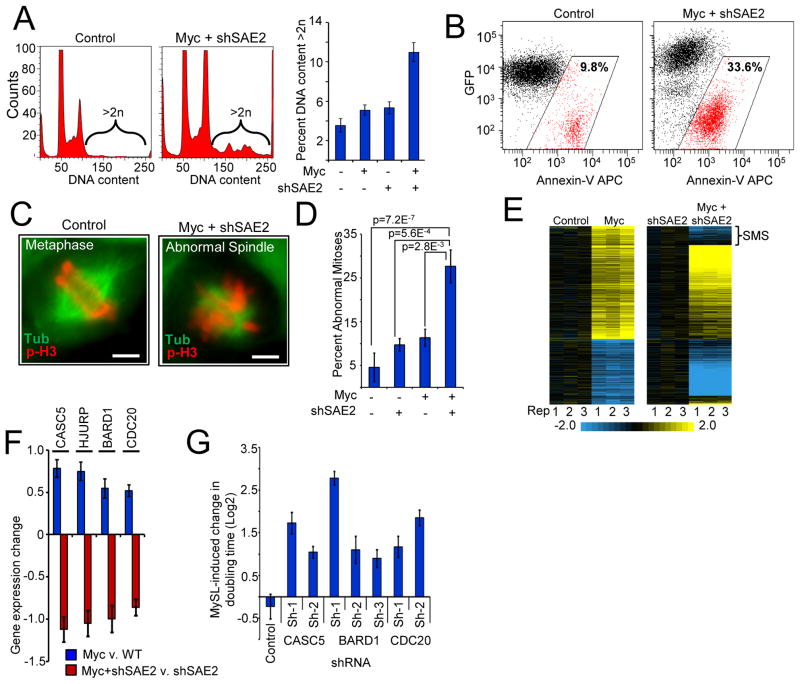
Figure 3. Inactivation of SAE2 switches the Myc transcriptional program and dysregulates mitotic fidelity and cell viability.
a) Ectopic Myc activation and SAE2 inactivation leads to increase in G2/M cells and aberrant chromosomal content. Myc-ER HMECs transduced with inducible shSAE2 were cultured −/+ Myc-ER-induction (24 h) and −/+ shSAE2 induction. Cells were analyzed for DNA content by flow cytometry (quantification of cells with >2N DNA, right panel).
b) Depletion of SAE2 induces apoptosis in cooperation with Myc hyper-activation. pINDUCER-mir-SAE2-eGFP Myc-ER HMECs were cultured −/+ Myc-ER-induction and −/+ shSAE2 induction (48 h). The cells were analyzed for apoptosis (Annexin-V) by flow cytometry.
c) and d) Myc-SAE2 genetic interaction leads to defects in the mitotic spindle. Myc-ER HMECs transduced with inducible shRNA-SAE2 were cultured −/+ Myc-ER-induction (16 h) and −/+ shSAE2 induction. Cells were stained for Tubulin (green) and phospho-H3 (red) to visualize mitotic defects. Images from c) were quantified for both total and abnormal mitotic events d). Data are represented as percent abnormal mitoses (at least 100 mitotic events counted per condition; p -values from Fisher’s exact test). Scale bar=5uM
e) Loss of SAE2 alters the transcriptional response to Myc. HMECs expressing Myc-ER and dox-inducible SAE2-shRNA were analyzed by gene expression profiling −/+ Myc-ER-induction and −/+ SAE2-shRNA induction. All mRNAs altered by Myc-ER-induction (p < 0.05, 2-fold) are shown. The effect of Myc-ER-induction on mRNA levels in the absence or presence of shRNA-SAE2-induction are shown (left and right panels, respectively). mRNAs that change their response to Myc in the presence or absence of shSAE2 are termed “Sumoylation-dependent Myc switchers,” or SMS genes.
f) Loss of SAE2 alters Myc control of spindle-regulatory genes. The effect of Myc in the absence or presence of shSAE2 (blue and red bars, respectively) is shown for top 4 of 17 SMS genes with known roles in spindle integrity and function (see Fig. S9B for list of 17).
g) SMS genes are required to tolerate Myc hyper-activation. Myc-ER HMECs transduced with shRNAs targeting the indicated SMS genes were cultured −/+ Myc-ER-induction for 6 d. Cell numbers were counted and analyzed as in Fig 2A.