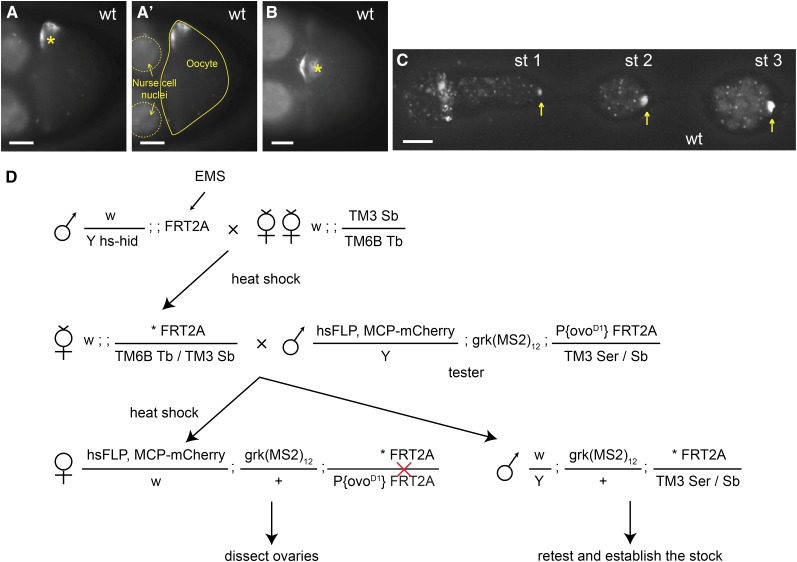
Figure 1.
Genetic screen based on in vivo RNA imaging. (A−C) grk transcript localization in wild-type egg-chambers. (A, B) Localization of grk*mCherry (MCP-labeled grk transcripts) as visualized in differently orientated stage 8−9 wild-type oocytes: the nucleus (asterisk) is at the side or at the top center of the anterior end in A and B, respectively. (A′) Same image as in (A) outlining the oocyte (solid line) and two nurse cell nuclei (dashed lines). (C) grk*mCherry in the germarium and stage 1−3 egg-chambers. grk*mCherry localizes to the wild-type oocyte, which is at the posterior of the egg-chambers (yellow arrows). (D) Crossing scheme for generating mosaic females with homozygous mutant germline. Asterisk indicates the mutagenized chromosome. hs-hid males are selectively eliminated by heat shock during larval stages. The red cross indicates a FLP-induced mitotic recombination event between the two FRT sequences. All developing egg-chambers are homozygous for induced mutations on 3L, because they lack the dominant female-sterile ovoD1 gene. Scale bars = 20 μm.