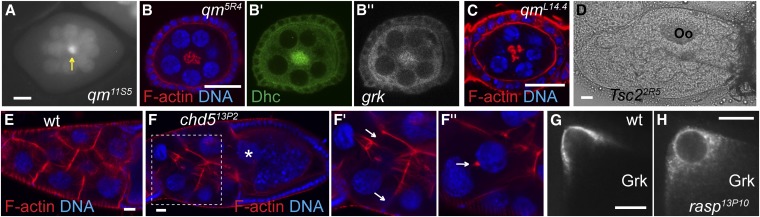
Figure 3.
Phenotypes of other mutants identified in the screen. (A) grk*mCherry localizes to the center of the qm11S5 egg-chamber (arrow). (B−B′′) Clustering of ring canals in center of qm5R4 oocytes as revealed by coincident central staining of mutant oocyte for F-actin (phalloidin, B), Dynein heavy chain (Dhc, B′), and grk*mCherry (grk, B′′). The lack of F-actin staining between nurse cell nuclei suggests that the cell membranes have collapsed. (C) Staining of F-actin (phalloidin) in qmL14.4 germline clone. (D) Laterally mispositioned oocyte (Oo) in a Tsc22R5 mutant stage 7−9 egg-chamber. (E, F) Phalloidin staining of wild-type (E) and Chd513P2 (F) stage 10B egg-chambers showing discontinuous actin filaments (arrows in F′) and a nurse cell nucleus (asterisk) going beyond the border of nurse cells and the oocyte. A different z-section of the same egg-chamber shows a collapsed ring canal (arrow in F′′). (G, H) Grk protein is more diffuse in the cytoplasm of rasp13P10 (H) than wild-type (G) stage 8−9 egg-chambers. scale bars = 20 μm.