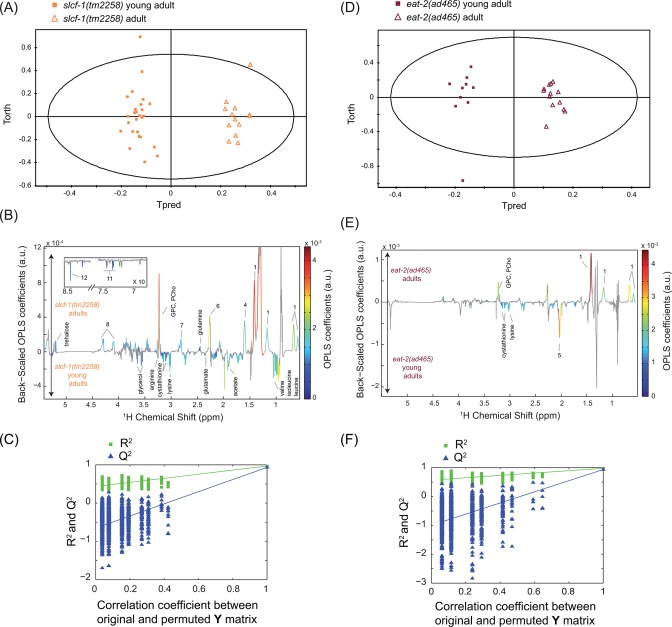
Figure 4.
Metabolic signatures of aging in slcf-1(tm2258) and eat-2(ad465)C. elegans worms. OPLS model discriminating slcf-1(tm2258) young adults and slcf-1(tm2258) adults (1 predictive component and 3 orthogonal components; R2X = 0.794, R2Y = 0.97, Q2 = 0.934) from Pareto-scaled data set: (A) scores plot; (B) loadings plot resulting from the SRV analysis; and (C) model validation resulting from 1000 permutations, demonstrating the model robustness, because model R2 and Q2 values were significantly higher than random model ones. OPLS model discriminating eat-2(ad465) young adults and eat-2(ad465) adults (1 predictive component and 2 orthogonal components; R2X = 0.728, R2Y = 0.978, Q2 = 0.934) from Pareto-scaled data set: (D) scores plot; (E) corresponding loadings plot resulting from the SRV analysis; and (F) model validation resulting from 1000 permutations, demonstrating the model robustness. Key: 1, cyclic fatty acids; 4, lipids (CH2CH2CO); 5, unsaturated lipids (CH2CH=CH); 6, lipids (CH2CO); 7, unsaturated lipids (CH=CHCH2CH=CH); 8, glyceryl of lipids; 11, phenylalanine; 12, formate; PCho, phosphocholine; GPC, glycerophosphocholine.