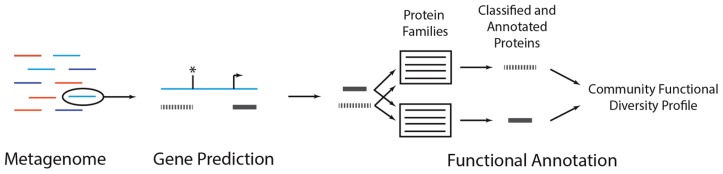
FIGURE 3.
A metagenomic functional annotation workflow. A metagenome (colored lines, left) can be annotated by subjecting each reads to gene prediction and functional annotation. In gene prediction, various algorithms can be used to identify subsequences in a metagenomic read (blue line) that may encode proteins (gray bars). In some situations, coding sequences may start (arrow) or stop (asterisk) upstream or downstream the length of the read, resulting in partial gene predictions. Each predicted protein can then be subject to functional annotation, wherein it is compared to a database of protein families. Predicted peptides that are classified as homologs of the family are annotated with the family’s function. Conducting this analysis across all reads results in a community functional diversity profile. As discussed in the main text, there are alternative annotation strategies and variations on this general procedure.