Figure 4. Mechanism of sulfenamide formation in protein tyrosine phosphatase B1 (PTPB1).
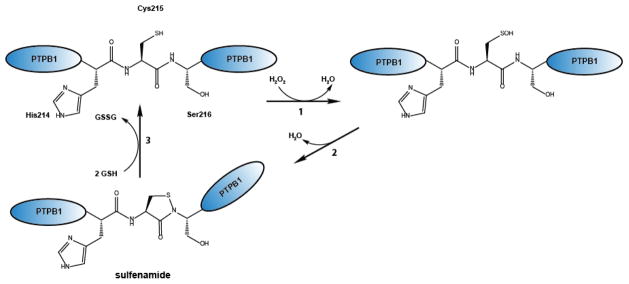
(1) Exposure of the catalytic cysteine 215 (RSH) of PTPB1 to H2O2 leads to the formation of a sulfenic acid (RSOH), which undergoes (2) intramolecular cyclization with a nearby amino group, yielding in sulfenamide (RSNR). (3) Reduction of the sulfenamide is mediated by forming a mixed disulfide formation with glutathione, which is subsequently resolved by glutaredoxin.
