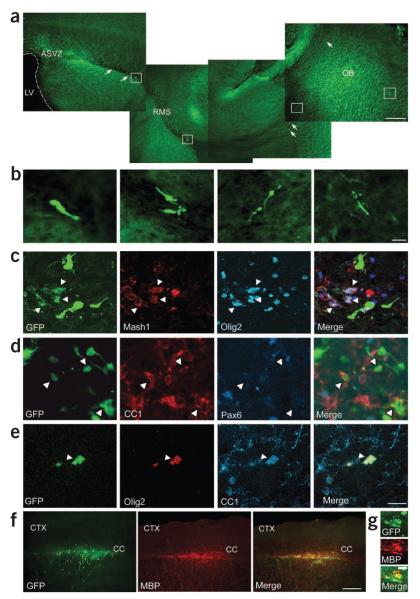
Figure 2.
Demyelination alters the migratory pathway and phenotype of GAD65-GFP–positive cells. (a) Confocal images of a sagittal brain section showing migratory pathway of GAD65-GFP–positive progenitor cells from the SVZ to the olfactory bulb (OB) along the RMS. Under normal conditions, GAD65-GFP–positive cells were found exclusively in the olfactory bulb; none migrated to the corpus callosum. Scale bar represents 400 μm. (b) Magnification of RMS GAD65-GFP–positive cells in white boxes, showing their neuronal morphology. Scale bar represents 20 μm. (c–e) At 14 dpl GAD65-GFP–positive cells in demyelinated corpus callosum coexpressed Mash1, Olig2 and CC1, but not Pax6. White arrowheads indicate GAD65-GFP–positive cells colabeled with different markers. Scale bar represents 20 μm. (f) Images show GAD65-GFP–positive cells immunolabeled with antibody to MBP in demyelinated corpus callosum at 14 dpl. CTX, cerebral cortex. Scale bar represents 400 μm. (g) Higher magnification of GAD65-GFP–positive cells colabeled with antibody to MBP in demyelinated corpus callosum. Scale bar represents 400 μm.